Mir-21 Suppression Promotes Mouse Hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 34638467
- PMCID: PMC8508272
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13194983
Mir-21 Suppression Promotes Mouse Hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
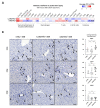
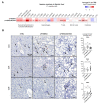
The microRNA 21 (miR-21) is upregulated in almost all known human cancers and is considered a highly potent oncogene and potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment. In the liver, miR-21 was reported to promote hepatic steatosis and inflammation, but whether miR-21 also drives hepatocarcinogenesis remains poorly investigated in vivo. Here we show using both carcinogen (Diethylnitrosamine, DEN) or genetically (PTEN deficiency)-induced mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), total or hepatocyte-specific genetic deletion of this microRNA fosters HCC development-contrasting the expected oncogenic role of miR-21. Gene and protein expression analyses of mouse liver tissues further indicate that total or hepatocyte-specific miR-21 deficiency is associated with an increased expression of oncogenes such as Cdc25a, subtle deregulations of the MAPK, HiPPO, and STAT3 signaling pathways, as well as alterations of the inflammatory/immune anti-tumoral responses in the liver. Together, our data show that miR-21 deficiency promotes a pro-tumoral microenvironment, which over time fosters HCC development via pleiotropic and complex mechanisms. These results question the current dogma of miR-21 being a potent oncomiR in the liver and call for cautiousness when considering miR-21 inhibition for therapeutic purposes in HCC.
Keywords: HCC; PTEN; fibrosis; immune cells; inflammation; microRNA 21; oncogenes; tumor suppressors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

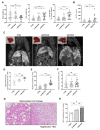
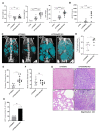
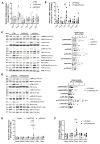
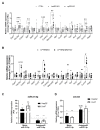

References
-
- Younossi Z., Stepanova M., Ong J.P., Jacobson I.M., Bugianesi E., Duseja A., Eguchi Y., Wong V.W., Negro F., Yilmaz Y., et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is the Fastest Growing Cause of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Liver Transplant Candidates. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018;17:748–755. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.057. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marrone A.K., Shpyleva S., Chappel G., Tryndyak V., Uehara T., Tsuchiya M., Beland F.A., Rusyn I., Pogribny I.P. Differentially Expressed MicroRNAs Provide Mechanistic Insight into Fibrosis-Associated Liver Carcinogenesis in Mice. Mol. Carcinog. 2015;55:808–817. doi: 10.1002/mc.22323. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

