The Expanding Role of Alternative Splicing in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Plasticity
- PMID: 34638554
- PMCID: PMC8508619
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms221910213
The Expanding Role of Alternative Splicing in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Plasticity
Abstract
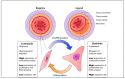
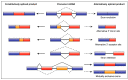
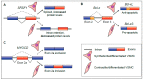
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) display extraordinary phenotypic plasticity. This allows them to differentiate or dedifferentiate, depending on environmental cues. The ability to 'switch' between a quiescent contractile phenotype to a highly proliferative synthetic state renders VSMCs as primary mediators of vascular repair and remodelling. When their plasticity is pathological, it can lead to cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and restenosis. Coinciding with significant technological and conceptual innovations in RNA biology, there has been a growing focus on the role of alternative splicing in VSMC gene expression regulation. Herein, we review how alternative splicing and its regulatory factors are involved in generating protein diversity and altering gene expression levels in VSMC plasticity. Moreover, we explore how recent advancements in the development of splicing-modulating therapies may be applied to VSMC-related pathologies.
Keywords: alternative splicing; cardiovascular disease; gene expression; splicing-modulating therapies; vascular smooth muscle cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chappell J., Harman J.L., Narasimhan V.M., Yu H., Foote K., Simons B.D., Bennett M.R., Jørgensen H.F. Extensive proliferation of a subset of differentiated, yet plastic, medial vascular smooth muscle cells contributes to neointimal formation in mouse injury and atherosclerosis models. Circ. Res. 2016;119:1313–1323. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.309799. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

