Effects of Substitution on Cytotoxicity of Diphenyl Ditelluride in Cultured Vascular Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 34638861
- PMCID: PMC8531998
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms221910520
Effects of Substitution on Cytotoxicity of Diphenyl Ditelluride in Cultured Vascular Endothelial Cells
Abstract
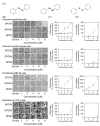
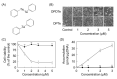
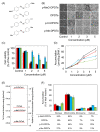
Among organic-inorganic hybrid molecules consisting of organic structure(s) and metal(s), only few studies are available on the cytotoxicity of nucleophilic molecules. In the present study, we investigated the cytotoxicity of a nucleophilic organotellurium compound, diphenyl ditelluride (DPDTe), using a cell culture system. DPDTe exhibited strong cytotoxicity against vascular endothelial cells and fibroblasts along with high intracellular accumulation but showed no cytotoxicity and had less accumulation in vascular smooth muscle cells and renal epithelial cells. The cytotoxicity of DPDTe decreased when intramolecular tellurium atoms were replaced with selenium or sulfur atoms. Electronic state analysis revealed that the electron density between tellurium atoms in DPDTe was much lower than those between selenium atoms of diphenyl diselenide and sulfur atoms of diphenyl disulfide. Moreover, diphenyl telluride did not accumulate and exhibit cytotoxicity. The cytotoxicity of DPDTe was also affected by substitution. p-Dimethoxy-DPDTe showed higher cytotoxicity, but p-dichloro-DPDTe and p-methyl-DPDTe showed lower cytotoxicity than that of DPDTe. The subcellular distribution of the compounds revealed that the compounds with stronger cytotoxicity showed higher accumulation rates in the mitochondria. Our findings suggest that the electronic state of tellurium atoms in DPDTe play an important role in accumulation and distribution of DPDTe in cultured cells. The present study supports the hypothesis that nucleophilic organometallic compounds, as well as electrophilic organometallic compounds, exhibit cytotoxicity by particular mechanisms.
Keywords: bio-organometallics; cytotoxicity; organoselenium compound; organotellurium compound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Grignard V. Regarding some new organometallic combinations of magnesium and their application to alcohol synthesis and hydrocarbides. CR Acad. Sci. 1900;130:1322–1324.
-
- Hara T., Matsuzaki H., Nakamura T., Yoshida E., Ohkubo T., Maruyama H., Yamamoto C., Saito S., Kaji T. Cytotoxicity of zinc, copper and rhodium complexes with 1, 10-phenanthroline or 2, 9-dimethyl-1, 10-phenanthroline in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2016;3:109–113. doi: 10.2131/fts.3.109. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

