Innovations in Health Care-A Conceptual Framework
- PMID: 34639328
- PMCID: PMC8508443
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph181910026
Innovations in Health Care-A Conceptual Framework
Abstract
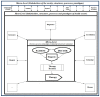
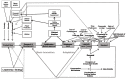
Innovations are the source of all human development and improvement of quality of life. At the same time, they challenge existing standards, solutions and societal patterns. In health care in particular, innovations enable us to treat previously incurable diseases or to make better use of scarce resources. However, they also make existing health care technologies obsolete, force specialists to learn completely new methods and require high investments. Consequently, in this paper we develop a conceptual framework model for the development, adoption and diffusion of innovations in health care. We analyse barriers and promoters of innovations, in particular meta-stability, costs, innovative ability and leadership and apply the framework to three innovations: personalized medicine, digital health, and implants. We conclude that strategic innovation management in healthcare is a prerequisite of the rapid development and adoption of innovations and the improvement of quality of life of the (aging) population.
Keywords: adoption; diffusion; digital health; e-health; implant; innovation; innovation management; personalized medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hauschildt J., Salomo S., Schultz C., Kock A. Innovationsmanagement. Vahlen; München, Germany: 2016.
-
- Verspagen B. The Oxford Handbook of Innovation. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2005. Innovation and economic growth.
-
- Schumpeter J. The Theory of Economic Development. Duncker & Humblot; Leipzig, Germany: 1934.
-
- Vahs D., Brem A. Innovationsmanagement: Von der Idee zur Erfolgreichen Vermarktung. 4th ed. Schäffer-Poeschel Verlag; Stuttgart, Germany: 2015.
-
- Feldman M.P. The Geography of Innovation. Kluwer Academic; Dortbrecht, The Netherlands: Boston, MA, USA: London, UK: 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

