Sensitivity Analysis Using a Reduced Finite Element Model for Structural Damage Identification
- PMID: 34639906
- PMCID: PMC8509307
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14195514
Sensitivity Analysis Using a Reduced Finite Element Model for Structural Damage Identification
Abstract
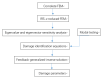
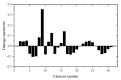
Sensitivity analysis is widely used in engineering fields, such as structural damage identification, model correction, and vibration control. In general, the existing sensitivity calculation formulas are derived from the complete finite element model, which requires a large amount of calculation for large-scale structures. In view of this, a fast sensitivity analysis algorithm based on the reduced finite element model is proposed in this paper. The basic idea of the proposed sensitivity analysis algorithm is to use a model reduction technique to avoid the complex calculation required in solving eigenvalues and eigenvectors by the complete model. Compared with the existing sensitivity calculation formulas, the proposed approach may increase efficiency, with a small loss of accuracy of sensitivity analysis. Using the fast sensitivity analysis, the linear equations for structural damage identification can be established to solve the desired elemental damage parameters. Moreover, a feedback-generalized inverse algorithm is proposed in this work in order to improve the calculation accuracy of damage identification. The core principle of this feedback operation is to reduce the number of unknowns, step by step, according to the generalized inverse solution. Numerical and experimental examples show that the fast sensitivity analysis based on the reduced model can obtain almost the same results as those obtained by the complete model for low eigenvalues and eigenvectors. The feedback-generalized inverse algorithm can effectively overcome the ill-posed problem of the linear equations and obtain accurate results of damage identification under data noise interference. The proposed method may be a very promising tool for sensitivity analysis and damage identification based on the reduced finite element model.
Keywords: damage identification; eigenvalue; eigenvector; feedback-generalized inverse; reduced model; sensitivity analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Huynh T.C., Park J.H., Kim J.T. Structural identification of cable-stayed bridge under back-to-back typhoons by wireless vibration monitoring. Measurement. 2016;88:385–401. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2016.03.032. - DOI
-
- Sharma G.S., Faverjon B., Dureisseix D., Skvortsov A., MacGillivray I., Audoly C., Kessissoglou N. Acoustic Performance of a Periodically Voided Viscoelastic Medium With Uncertainty in Design Parameters. J. Vib. Acoust. 2020;142:1–23. doi: 10.1115/1.4046859. - DOI
-
- Liu H.F., Li Z.G. An improved generalized flexibility matrix approach for structural damage detection. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2019;28:877–893. doi: 10.1080/17415977.2019.1683174. - DOI
-
- Yang Q.W. A new damage identification method based on structural flexibility disassembly. J. Vib. Control. 2011;17:1000–1008. doi: 10.1177/1077546309360052. - DOI
-
- Lu Z.R., Zhou J.X., Wang L. On choice and effect of weight matrix for response sensitivity-based damage identification with model and measurement errors. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019;114:1–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.05.007. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

