Reduction Mammoplasty: A Ten-Year Retrospective Review of the Omega Resection Pattern Technique
- PMID: 34640438
- PMCID: PMC8509280
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10194418
Reduction Mammoplasty: A Ten-Year Retrospective Review of the Omega Resection Pattern Technique
Abstract
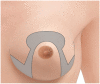
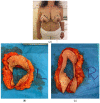
Reduction mammoplasty is the gold standard procedure for symptomatic breast hypertrophy and it is also used for contralateral breast symmetrisation following breast cancer surgery. We aim at introducing a new procedure, which uses an omega resection pattern to simplify the inferior pedicle breast resection technique. A retrospective review of all patients who underwent the omega resection reduction mammoplasty at the University Hospital of Basel between 2010 and 2020 was carried out. We collected patient demographics, surgical outcomes, operation time, type and frequency of complications at 12 months follow-up. Outcomes were compared with the most commonly used techniques. Additionally, we assessed if patients' and clinical characteristics augmented/diminished the complication rate. During the study period, 67 reduction mammaplasties were performed by a senior plastic surgeon (Mage = 42.5, SDage = 15.6; MBMI = 27.28, SDBMI = 3.4; 20% smokers). The average tissue removed was 826 g (ranging from 15 to 2307 g). In 10 breasts (15%) occurred minor complications. No major complications were reported. Operation time (M = 149 min; ranging from 87 to 270 min) was significantly shorter than the inferior, superomedial, and superior pedicle techniques. Univariate Odd Ratios showed that no-smoker status, a BMI in a normal range, resection weight between 500 g to 1500 g, NTN distance < 30 cm, removal of drains one day after the operation, ASA index of 2, inpatient clinic hospitalisation, and not undergoing other concomitant surgical operations were protective factors against the risk to develop complications. The omega resection pattern technique demonstrated to be an effective, safe, and fast mammoplasty reduction procedure for bilateral macromastia and unilateral symmetrizing procedures, even for large breasts, able to be adopted as a new valid alternative to the existing ones.
Keywords: hypermastia; omega resection; reduction mammoplasty; retrospective; symmetrisation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

