The Impact of COVID-19 on Kidney Transplant Recipients in Pre-Vaccination and Delta Strain Era: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34640552
- PMCID: PMC8509345
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10194533
The Impact of COVID-19 on Kidney Transplant Recipients in Pre-Vaccination and Delta Strain Era: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
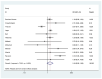
Herein, we performed a meta-analysis of published clinical outcomes of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in hospitalized kidney transplant recipients. A systematic database search was conducted between December 1, 2019 and April 20, 2020. We analyzed 48 studies comprising 3137 kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19. Fever (77%), cough (65%), dyspnea (48%), and gastrointestinal symptoms (28%) were predominant on hospital admission. The most common comorbidities were hypertension (83%), diabetes mellitus (34%), and cardiac disease (23%). The pooled prevalence of acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute kidney injury were 58% and 48%, respectively. Invasive ventilation and dialysis were required in 24% and 22% patients, respectively. In-hospital mortality rate was as high as 21%, and increased to over 50% for patients in intensive care unit (ICU) or requiring invasive ventilation. Risk of mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), on mechanical ventilation, and ICU admission was increased: OR = 19.59, OR = 3.80, and OR = 13.39, respectively. Mortality risk in the elderly was OR = 3.90; however, no such association was observed in terms of time since transplantation and gender. Fever, cough, dyspnea, and gastrointestinal symptoms were common on admission for COVID-19 in kidney transplant patients. Mortality was as high as 20% and increased to over 50% in patients in ICU and required invasive ventilation.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; kidney transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
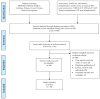
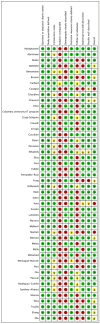




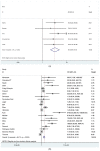

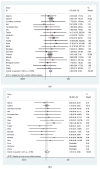

References
-
- Zheng K.I., Gao F., Wang X.-B., Sun Q.-F., Pan K.-H., Wang T.-Y., Ma H.-L., Chen Y.-P., Liu W.-Y., George J., et al. Letter to the Editor: Obesity as a Risk Factor for Greater Severity of COVID-19 in Patients with Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Metabolism. 2020;108:154244. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

