Evolution of the Use of Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients in Spain between March and November 2020: SEMI-COVID National Registry
- PMID: 34640628
- PMCID: PMC8509849
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10194610
Evolution of the Use of Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients in Spain between March and November 2020: SEMI-COVID National Registry
Abstract
Objectives: Since the results of the RECOVERY trial, WHO recommendations about the use of corticosteroids (CTs) in COVID-19 have changed. The aim of the study is to analyse the evolutive use of CTs in Spain during the pandemic to assess the potential influence of new recommendations.
Material and methods: A retrospective, descriptive, and observational study was conducted on adults hospitalised due to COVID-19 in Spain who were included in the SEMI-COVID-19 Registry from March to November 2020.
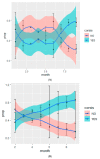
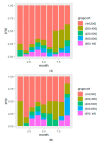
Results: CTs were used in 6053 (36.21%) of the included patients. The patients were older (mean (SD)) (69.6 (14.6) vs. 66.0 (16.8) years; p < 0.001), with hypertension (57.0% vs. 47.7%; p < 0.001), obesity (26.4% vs. 19.3%; p < 0.0001), and multimorbidity prevalence (20.6% vs. 16.1%; p < 0.001). These patients had higher values (mean (95% CI)) of C-reactive protein (CRP) (86 (32.7-160) vs. 49.3 (16-109) mg/dL; p < 0.001), ferritin (791 (393-1534) vs. 470 (236-996) µg/dL; p < 0.001), D dimer (750 (430-1400) vs. 617 (345-1180) µg/dL; p < 0.001), and lower Sp02/Fi02 (266 (91.1) vs. 301 (101); p < 0.001). Since June 2020, there was an increment in the use of CTs (March vs. September; p < 0.001). Overall, 20% did not receive steroids, and 40% received less than 200 mg accumulated prednisone equivalent dose (APED). Severe patients are treated with higher doses. The mortality benefit was observed in patients with oxygen saturation </=90%.
Conclusions: Patients with greater comorbidity, severity, and inflammatory markers were those treated with CTs. In severe patients, there is a trend towards the use of higher doses. The mortality benefit was observed in patients with oxygen saturation </=90%.
Keywords: COVID-19; Spain; comorbidities; corticosteroids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) [(accessed on 30 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-manageme....
-
- Long Y., Xu Y., Wang B., Zhang L., Jia D., Xue F., Duan G., He J., Xia J.-Y., Xu D. Clinical Recommendations from an Observational Study on MERS: Glucocorticoids was Benefit in Treating SARS Patients. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016;9:8865–8873.
-
- Lee N., Chan K.A., Hui D., Ng E.K., Wu A., Chiu R.W., Wong V.W., Chan P., Wong K., Wong E., et al. Effects of Early Corticosteroid Treatment on Plasma SARS-Associated Coronavirus RNA Concentrations in Adult Patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2004;31:304–309. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2004.07.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

