Cardiometabolic Disorders and the Risk of Critical COVID-19 as Compared to Influenza Pneumonia
- PMID: 34640638
- PMCID: PMC8509116
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10194618
Cardiometabolic Disorders and the Risk of Critical COVID-19 as Compared to Influenza Pneumonia
Abstract
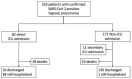
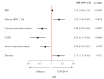
We aimed to compare the influence of cardiometabolic disorders on the incidence of severe COVID-19 vs. non-COVID pneumonia. We included all consecutive patients admitted with SARS-CoV-2-positive pneumonia between 12 March 2020 and 1 April 2020 and compared them to patients with influenza pneumonia hospitalized between December 2017 and December 2019 at the same tertiary hospital in Paris. Patients with COVID-19 were significantly younger and more frequently male. In the analysis adjusted for age and sex, patients with COVID-19 were more likely to be obese (adjOR: 2.25; 95% CI 1.24-4.09; p = 0.0076) and receive diuretics (adjOR: 2.13; 95% CI 1.12-4.03; p = 0.021) but were less likely to be smokers (adjOR: 0.40; 95% CI 0.24-0.64; p = 0.0002), have COPD (adjOR: 0.25; 95% CI 0.11-0.56; p = 0.0008), or have a previous or active cancer diagnosis (adjOR: 0.54, 95% CI 0.32-0.91; p = 0.020). The rate of ICU admission was significantly higher in patients with COVID-19 (32.4% vs. 5.2% p < 0.0001). Obesity was significantly associated with the risk of direct ICU admission in patients with COVID-19 but not in patients with influenza pneumonia. Likewise, pre-existing hypertension was significantly associated with mortality in patients with COVID-19 but not in patients with influenza pneumonia. Cardiometabolic disorders differentially influenced the risk of presenting with severe COVID-19 or influenza pneumonia.
Keywords: COVID-19; cardiovascular risk factors; hypertension; obesity; seasonal influenza.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simonnet A., Chetboun M., Poissy J., Raverdy V., Noulette J., Duhamel A., Labreuche J., Mathieu D., Pattou F., Jourdain M., et al. High Prevalence of Obesity in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Requiring Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2020;28:1195–1199. doi: 10.1002/oby.22831. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Petrilli C.M., Jones S.A., Yang J., Rajagopalan H., O’Donnell L., Chernyak Y., Tobin K.A., Cerfolio R.J., Francois F., Horwitz L.I. Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: Prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1966. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1966. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

