Sensor Size Effect on Rayleigh Wave Velocity on Cementitious Surfaces
- PMID: 34640801
- PMCID: PMC8512871
- DOI: 10.3390/s21196483
Sensor Size Effect on Rayleigh Wave Velocity on Cementitious Surfaces
Abstract
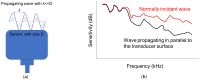
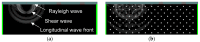
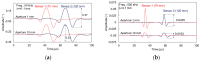
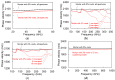
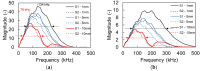
Concrete properties and damage conditions are widely evaluated by ultrasonics. When access is limited, the evaluation takes place from a single surface. In this case, the sensor size plays a crucial role due to the "aperture effect". While this effect is well documented regarding the amplitude or the frequency content of the surface (or Rayleigh) wave pulses, it has not been studied in terms of the wave velocity, although the velocity value is connected to concrete stiffness, porosity, damage degree, and is even empirically used to evaluate compressive strength. In this study, numerical simulations take place where sensors of different sizes are used to measure the surface wave velocity as well as its dependence on frequency (dispersion) and sensor size, showing the strong aperture effect and suggesting rules for reliable measurements on a concrete surface. The numerical trends are also validated by experimental measurements on a cementitious material by sensors of different sizes.
Keywords: aperture effect; concrete; dispersion; heterogeneity; sensor size; surface (Rayleigh) waves.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






References
-
- Naik T., Malhotra V., Popovics J. Handbook on Nondestructive Testing of Concrete. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2003. The Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Method; pp. 8–11.
-
- Landis E., Shah P. Frequency-dependent stress wave attenuation in cement-based materials. J. Eng. Mech. 1995;121:737–743. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1995)121:6(737). - DOI
-
- Iliopoulos S., De Smet L., Aggelis D. Investigating ultrasonic wave dispersion and attenuation in fresh cementitious materials: A combined numerical, analytical, and experimental approach. NDT E Int. 2018;100:115–123. doi: 10.1016/j.ndteint.2018.09.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

