A Hierarchical Approach to Activity Recognition and Fall Detection Using Wavelets and Adaptive Pooling
- PMID: 34640974
- PMCID: PMC8512095
- DOI: 10.3390/s21196653
A Hierarchical Approach to Activity Recognition and Fall Detection Using Wavelets and Adaptive Pooling
Abstract
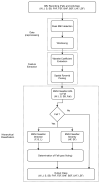
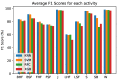
Human activity recognition has been a key study topic in the development of cyber physical systems and assisted living applications. In particular, inertial sensor based systems have become increasingly popular because they do not restrict users' movement and are also relatively simple to implement compared to other approaches. In this paper, we present a hierarchical classification framework based on wavelets and adaptive pooling for activity recognition and fall detection predicting fall direction and severity. To accomplish this, windowed segments were extracted from each recording of inertial measurements from the SisFall dataset. A combination of wavelet based feature extraction and adaptive pooling was used before a classification framework was applied to determine the output class. Furthermore, tests were performed to determine the best observation window size and the sensor modality to use. Based on the experiments the best window size was found to be 3 s and the best sensor modality was found to be a combination of accelerometer and gyroscope measurements. These were used to perform activity recognition and fall detection with a resulting weighted F1 score of 94.67%. This framework is novel in terms of the approach to the human activity recognition and fall detection problem as it provides a scheme that is computationally less intensive while providing promising results and therefore can contribute to edge deployment of such systems.
Keywords: Internet of Things (IoT); activity recognition; artificial intelligence; cyber physical systems; direction and severity; fall detection; smart health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ozcan K., Mahabalagiri A.K., Casares M., Velipasalar S. Automatic fall detection and activity classification by a wearable embedded smart camera. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2013;3:125–136. doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2013.2256832. - DOI
-
- WHO . Falls: Key Facts. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021.
-
- CDC . Keep on Your Feet—Preventing Older Adult Falls | CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2021.
-
- Nations U. In: World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, Key Findings and Advance Tables. Department of Economics and Social Affairs PD, editor. United Nations; New York, NY, USA: 2017.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical