Peptide Conjugate on Multilayer Graphene Oxide Film for the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 34641106
- PMCID: PMC8512023
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13193290
Peptide Conjugate on Multilayer Graphene Oxide Film for the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
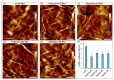
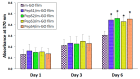
Graphene oxide (GO) is extensively studied as a template material for mesenchymal stem cell application due to its two-dimensional nature and unique functionalization chemistries. Herein, a new type of peptide-conjugated multilayer graphene oxide (peptide/m-GO film) was fabricated and used as biomaterial for culturing human Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells (WJ-MSCs). The characterization of the peptide/m-GO films was performed, and the biocompatibility of the WJ-MSCs on the peptide/m-GO films was investigated. The results demonstrated that the peptide conjugate on the m-GO film did not hamper the normal growth of WJ-MSCs but supported the growth of WJ-MSCs after the 6-day culture period. In addition, the osteogenic differentiation of WJ-MSCs on the peptide/m-GO films was enhanced as compared with the parent m-GO film. Therefore, such peptide-conjugated m-GO films could provide a highly biocompatible and multifunctional 2D material to tailor the potential application of WJ-MSCs in bone tissue regeneration.
Keywords: Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells; multilayer graphene oxide; osteogenic differentiation; peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential gene expression of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal cells mediated by graphene oxide in basal and osteo-induced media.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Mar 3;51(1):383. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09324-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38433142
-
Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue and Wharton's jelly of the umbilical cord.Acta Biochim Pol. 2017;64(2):365-369. doi: 10.18388/abp.2016_1488. Epub 2017 Jun 10. Acta Biochim Pol. 2017. PMID: 28600911
-
Chitosan/hyaluronic acid multilayer films are biocompatible substrate for Wharton's jelly derived stem cells.Stem Cell Investig. 2018 Dec 20;5:47. doi: 10.21037/sci.2018.12.02. eCollection 2018. Stem Cell Investig. 2018. PMID: 30701182 Free PMC article.
-
Osteogenic Induction of Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell for Bone Regeneration: A Systematic Review.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Nov 11;2018:2406462. doi: 10.1155/2018/2406462. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 30534156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics and clinical applications of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.Curr Res Transl Med. 2020 Jan;68(1):5-16. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 31543433 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hybrid Nano-Biointerface between Proteins/Peptides and Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials.Molecules. 2023 Oct 13;28(20):7064. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207064. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Graphene Derivatives as Artificial Extracellular Matrices on Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Molecules. 2022 Jan 7;27(2):379. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020379. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35056690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Graphene Oxide-Protein-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Mar 4;14(5):1032. doi: 10.3390/polym14051032. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive peptides and proteins for tissue repair: microenvironment modulation, rational delivery, and clinical potential.Mil Med Res. 2024 Dec 5;11(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00576-x. Mil Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39639374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of graphene quantum dots on osteogenesis potential of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells in fibrin hydrogel scaffolds.Cytotechnology. 2025 Feb;77(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00672-9. Epub 2024 Dec 10. Cytotechnology. 2025. PMID: 39665046
References
-
- Suman S., Domingues A., Ratajczak J., Ratajczak M.Z. Potential Clinical Applications of Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine. In: Ratajczak M.Z., editor. Stem Cells: Therapeutic Applications. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2019. pp. 1–22. - PubMed
-
- Contaldo M., De Rosa A., Nucci L., Ballini A., Malacrinò D., La Noce M., Inchingolo F., Xhajanka E., Ferati K., Bexheti-Ferati A., et al. Titanium Functionalized with Polylysine Homopolymers: In Vitro Enhancement of Cells Growth. Materials. 2021;14:3735. doi: 10.3390/ma14133735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stefania C., Vito C., Antonio B., Antonio E.U., Michele F., Giuseppe M., Patrizio B., Chiara D., Francesca F., Andrea B., et al. Recent Advances in Endocrine, Metabolic and Immune Disorders: Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) and Engineered Scaffolds. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets. 2018;18:466–469. doi: 10.2174/1871530318666180423102905. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

