Pimenta dioica (L.) Merr. Bioactive Constituents Exert Anti-SARS-CoV-2 and Anti-Inflammatory Activities: Molecular Docking and Dynamics, In Vitro, and In Vivo Studies
- PMID: 34641388
- PMCID: PMC8510437
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26195844
Pimenta dioica (L.) Merr. Bioactive Constituents Exert Anti-SARS-CoV-2 and Anti-Inflammatory Activities: Molecular Docking and Dynamics, In Vitro, and In Vivo Studies
Abstract
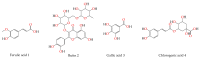
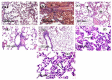
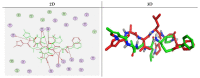
In response to the urgent need to control Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), this study aims to explore potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents from natural sources. Moreover, cytokine immunological responses to the viral infection could lead to acute respiratory distress which is considered a critical and life-threatening complication associated with the infection. Therefore, the anti-viral and anti-inflammatory agents can be key to the management of patients with COVID-19. Four bioactive compounds, namely ferulic acid 1, rutin 2, gallic acid 3, and chlorogenic acid 4 were isolated from the leaves of Pimenta dioica (L.) Merr (ethyl acetate extract) and identified using spectroscopic evidence. Furthermore, molecular docking and dynamics simulations were performed for the isolated and identified compounds (1-4) against SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) as a proposed mechanism of action. Furthermore, all compounds were tested for their half-maximal cytotoxicity (CC50) and SARS-CoV-2 inhibitory concentrations (IC50). Additionally, lung toxicity was induced in rats by mercuric chloride and the effects of treatment with P. dioca aqueous extract, ferulic acid 1, rutin 2, gallic acid 3, and chlorogenic acid 4 were recorded through measuring TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-10, G-CSF, and genetic expression of miRNA 21-3P and miRNA-155 levels to assess their anti-inflammatory effects essential for COVID-19 patients. Interestingly, rutin 2, gallic acid 3, and chlorogenic acid 4 showed remarkable anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities with IC50 values of 31 µg/mL, 108 μg/mL, and 360 µg/mL, respectively. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory effects were found to be better in ferulic acid 1 and rutin 2 treatments. Our results could be promising for more advanced preclinical and clinical studies especially on rutin 2 either alone or in combination with other isolates for COVID-19 management.
Keywords: Pimenta; anti-SARS-CoV-2; docking and dynamics simulations; in vitro and in vivo studies; rutin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigating the promising SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitory activity of secoiridoids isolated from Jasminum humile; in silico and in Vitro assessments with structure-activity relationship.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Aug;42(13):6941-6953. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2240419. Epub 2023 Jul 28. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37505066
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of Thai medicinal plants: in vitro screening and in silico docking of phytoconstituents for novel anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Jul 19;24(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04586-z. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39030504 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally Available Flavonoid Aglycones as Potential Antiviral Drug Candidates against SARS-CoV-2.Molecules. 2021 Oct 29;26(21):6559. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216559. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770969 Free PMC article.
-
Propolis, Bee Honey, and Their Components Protect against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review of In Silico, In Vitro, and Clinical Studies.Molecules. 2021 Feb 25;26(5):1232. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051232. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33669054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taming the storm: potential anti-inflammatory compounds targeting SARS-CoV-2 MPro.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Oct;32(5):3007-3035. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01525-9. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39048773 Review.
Cited by
-
Small molecules in the treatment of COVID-19.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Dec 5;7(1):387. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01249-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36464706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the potential anticancer activities of antibiotics as topoisomerase II inhibitors and DNA intercalators: in vitro, molecular docking, molecular dynamics, and SAR studies.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2171029. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2171029. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36701269 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-based design and synthesis of N'-Benzylidene-3,4-dimethoxybenzohydrazide derivatives as potential antimicrobial agents; evaluation by in vitro, in vivo, and in silico approaches with SAR studies.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):1098-1119. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2063282. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35430934 Free PMC article.
-
Spice-Derived Phenolic Compounds: Potential for Skin Cancer Prevention and Therapy.Molecules. 2023 Aug 25;28(17):6251. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176251. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Update of Various Attempts by Medicinal Chemists to Combat COVID-19 through Natural Products.Molecules. 2023 Jun 20;28(12):4860. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124860. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375415 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acter T., Uddin N., Das J., Akhter A., Choudhury T.R., Kim S. Evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A global health emergency. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020;730:138996. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138996. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Worldometer. 2021. [(accessed on 1 August 2021)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- Milanović Ž.B., Milanović Z., Antonijević M., Amić A.D., Avdovic E.H., Dimic D., Milenković D., Marković Z. Inhibitory activity of quercetin, its metabolite, and standard antiviral drugs towards enzymes essential for SARS-CoV-2: The role of acid–base equilibria. Rsc Adv. 2021;11:2838–2847. doi: 10.1039/D0RA09632F. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elebeedy D., Elkhatib W.F., Kandeil A., Ghanem A., Kutkat O., Alnajjar R., Saleh M.A., El Maksoud A.I.A., Badawy I., Al-Karmalawy A.A. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities of tanshinone IIA, carnosic acid, rosmarinic acid, salvianolic acid, baicalein, and glycyrrhetinic acid between computational and in vitro insights. RSC Adv. 2021;11:29267–29286. doi: 10.1039/D1RA05268C. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

