Grape Extract Promoted α-MSH-Induced Melanogenesis in B16F10 Melanoma Cells, Which Was Inverse to Resveratrol
- PMID: 34641503
- PMCID: PMC8512250
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26195959
Grape Extract Promoted α-MSH-Induced Melanogenesis in B16F10 Melanoma Cells, Which Was Inverse to Resveratrol
Abstract
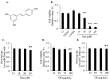
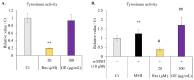
Melanin is a natural pigment produced by cells to prevent damage caused by ultraviolet radiation. Previously, resveratrol was shown to reduce melanin synthesis. As a natural polyphenol with various biological activities, resveratrol occurs in a variety of beverages and plant foods, such as grapes. Therefore, we investigated whether grape extracts containing resveratrol also had the ability to regulate melanin synthesis. In this study, we used mouse B16F10 melanoma cells as a model for melanin synthesis with the melanogenesis-inducing α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) as a positive control. Our results confirmed previous reports that resveratrol reduces melanin synthesis by reducing the activity of the rate-limiting enzyme tyrosinase. In contrast, the grape extract could not reduce melanin synthesis, and in fact promoted melanogenesis in the presence of α-MSH. The expression of genes related to melanin synthesis, such as tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein-1, tyrosinase-related protein-2, and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, also supports these phenomena, which means that even in the presence of resveratrol, grape extract will strengthen the function of α-MSH in promoting melanin synthesis. Therefore, these results also provide a point of view for research on cosmetics.
Keywords: B16F10 melanoma cells; grape extract; melanin synthesis; resveratrol; tyrosinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

