Synapse development is regulated by microglial THIK-1 K+ channels
- PMID: 34642249
- PMCID: PMC8545484
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2106294118
Synapse development is regulated by microglial THIK-1 K+ channels
Abstract
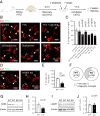
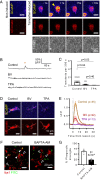
Microglia are the resident immune cells of the central nervous system. They constantly survey the brain parenchyma for redundant synapses, debris, or dying cells, which they remove through phagocytosis. Microglial ramification, motility, and cytokine release are regulated by tonically active THIK-1 K+ channels on the microglial plasma membrane. Here, we examined whether these channels also play a role in phagocytosis. Using pharmacological blockers and THIK-1 knockout (KO) mice, we found that a lack of THIK-1 activity approximately halved both microglial phagocytosis and marker levels for the lysosomes that degrade phagocytically removed material. These changes may reflect a decrease of intracellular [Ca2+]i activity, which was observed when THIK-1 activity was reduced, since buffering [Ca2+]i reduced phagocytosis. Less phagocytosis is expected to result in impaired pruning of synapses. In the hippocampus, mice lacking THIK-1 expression had an increased number of anatomically and electrophysiologically defined glutamatergic synapses during development. This resulted from an increased number of presynaptic terminals, caused by impaired removal by THIK-1 KO microglia. The dependence of synapse number on THIK-1 K+ channels, which control microglial surveillance and phagocytic ability, implies that changes in the THIK-1 expression level in disease states may contribute to altering neural circuit function.
Keywords: microglia; phagocytosis; synaptic pruning.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lawson L. J., Perry V. H., Dri P., Gordon S., Heterogeneity in the distribution and morphology of microglia in the normal adult mouse brain. Neuroscience 39, 151–170 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Izquierdo P., Attwell D., Madry C., Ion channels and receptors as determinants of microglial function. Trends Neurosci. 42, 278–292 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Brown G. C., Neher J. J., Microglial phagocytosis of live neurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 15, 209–216 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

