Esophageal Nocturnal Baseline Impedance and Post-reflux Swallow-induced Peristaltic Wave Index in Identifying Proton Pump Inhibitor-refractory Non-erosive Reflux Disease
- PMID: 34642272
- PMCID: PMC8521464
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm20073
Esophageal Nocturnal Baseline Impedance and Post-reflux Swallow-induced Peristaltic Wave Index in Identifying Proton Pump Inhibitor-refractory Non-erosive Reflux Disease
Abstract
Background/aims: Esophageal mean nocturnal baseline impedance (MNBI) levels and post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic wave (PSPW) index could increase the diagnostic value of 24-hour multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. This study aims to compare the MNBI and PSPW index in patients with no evidence of erosive reflux disease.
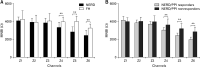
Methods: Impedance-pH monitoring tracings from 70 patients, 50 with non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) and 20 with functional heartburn (FH), were reviewed. According to proton pump inhibitors (PPI) treatment response, NERD patients were divided into NERD/PPI responders and NERD/PPI nonresponders. MNBI, PSPW index, and intercellular spaces were measured and compared among each group.
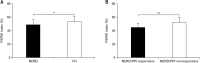
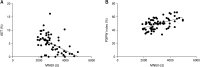
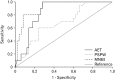
Results: MNBI values and PSPW index were lower in NERD patients than in FH (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively). MNBI positively correlated with PSPW index (r = 0.525, P < 0.001). NERD/PPI responders had lower MNBI values and PSPW index compared to NERD/PPI nonresponders (both P < 0.01). MNBI and PSPW index distinguished NERD from FH patients with an area under the curve of 0.914 and 0.677, respectively. Wider intercellular space could be identified in patients with NERD (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: MNBI and PSPW index may differentiate NERD from FH patients and relate to PPI treatment efficacy in patients with NERD.
Keywords: Electric impedance; Gastroesophageal reflux; Intercellular spaces; Proton pump inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical diagnostic value of mean nocturnal baseline impedance and post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic wave index for distinguishing functional heartburn from non-erosive reflux disease.Prz Gastroenterol. 2025;20(2):206-214. doi: 10.5114/pg.2024.142910. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Prz Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40620310 Free PMC article.
-
The added diagnostic value of postreflux swallow-induced peristaltic wave index and nocturnal baseline impedance in refractory reflux disease studied with on-therapy impedance-pH monitoring.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017 Mar;29(3). doi: 10.1111/nmo.12947. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017. PMID: 27620303
-
Analyses of the Post-reflux Swallow-induced Peristaltic Wave Index and Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Parameters Increase the Diagnostic Yield of Impedance-pH Monitoring of Patients With Reflux Disease.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jan;14(1):40-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.06.026. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26122764
-
Clinical use of mean nocturnal baseline impedance and post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic wave index for the diagnosis of gastro-esophageal reflux disease.Esophagus. 2022 Oct;19(4):525-534. doi: 10.1007/s10388-022-00933-6. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Esophagus. 2022. PMID: 35768671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impedance-pH Monitoring for Diagnosis of Reflux Disease: New Perspectives.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Aug;62(8):1881-1889. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4625-8. Epub 2017 May 26. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28550489 Review.
Cited by
-
Utility of the Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index and Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance for the Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Phenotypes in Children.Children (Basel). 2024 Jun 26;11(7):773. doi: 10.3390/children11070773. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062223 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical diagnostic value of mean nocturnal baseline impedance and post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic wave index for distinguishing functional heartburn from non-erosive reflux disease.Prz Gastroenterol. 2025;20(2):206-214. doi: 10.5114/pg.2024.142910. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Prz Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40620310 Free PMC article.
-
The Utility of Novel pH-Impedance Monitoring Parameters (PSPW Index and MNBI) in Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Phenotypes-A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Jun 6;13(11):3351. doi: 10.3390/jcm13113351. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38893061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The utility of balloon-based and standard impedance technology to diagnose esophageal mucosal diseases in children.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024 Mar;36(3):e14726. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14726. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024. PMID: 38129704 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between Conventional and Simple Measuring Methods of Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance in Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.Clin Pract. 2024 Aug 27;14(5):1682-1695. doi: 10.3390/clinpract14050134. Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 39311284 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

