Safety, tolerability and antiviral activity of the antisense oligonucleotide bepirovirsen in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a phase 2 randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 34642494
- PMCID: PMC8516644
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01513-4
Safety, tolerability and antiviral activity of the antisense oligonucleotide bepirovirsen in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a phase 2 randomized controlled trial
Abstract
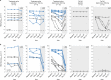
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) leads to an increased risk of death from cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Functional cure rates are low with current treatment options (nucleos(t)ide analogs (NAs) and pegylated interferons). Bepirovirsen is an antisense oligonucleotide targeting all HBV messenger RNAs; in cell culture and animal models, bepirovirsen leads to reductions in HBV-derived RNAs, HBV DNA and viral proteins. This phase 2 double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial is the first evaluation of the safety and activity of an antisense oligonucleotide targeting HBV RNA in both treatment-naïve and virally suppressed individuals with chronic HBV infection. The primary objective was to assess the safety and tolerability of bepirovirsen in individuals with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) (NCT02981602). The secondary objective was to assess antiviral activity, including the change from baseline to day 29 in serum hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) concentration. Participants with CHB infection ≥6 months and serum HBsAg ≥50 IU ml-1 were enrolled from seven centers across Hong Kong and the Republic of Korea and randomized (3:1 within each dose cohort) to receive bepirovirsen or placebo via subcutaneous injection twice weekly during weeks 1 and 2 (days 1, 4, 8 and 11) and once weekly during weeks 3 and 4 (days 15 and 22). Participants were then followed for 26 weeks. Twenty-four participants were treatment-naïve and seven were receiving stable NA therapy. Treatment-emergent adverse events were mostly mild/moderate (most commonly injection site reactions). Eleven (61.1%) and three (50.0%) treatment-naïve participants experienced one or more treatment-emergent adverse event in the bepirovirsen and placebo groups, respectively. In participants receiving NA therapy, the corresponding numbers were three (60.0%) and one (50.0%). Transient, self-resolving alanine aminotransferase flares (≥2× upper limit of normal) were observed in eight treatment-naïve participants and three participants on stable NA regimens in the bepirovirsen treatment arms. HBsAg reductions were observed and were significant versus placebo for treatment-naïve participants receiving bepirovirsen 300 mg (P = 0.001), but not for the bepirovirsen 150 mg group (P = 0.245) or participants receiving stable NA therapy (P = 0.762). Two participants in each of the 300 mg dose groups achieved HBsAg levels below the lower limit of quantitation by day 29 (n = 3) or day 36 (n = 1). Bepirovirsen had a favorable safety profile. These preliminary observations warrant further investigation of the safety and activity of bepirovirsen in a larger CHB patient population.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.-F.Y. has acted as a consultant for AbbVie, Arbutus Biopharma, Assembly Biosciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Clear B Therapeutics, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Springbank Pharmaceutical and Roche, and received grant/research support from Assembly Biosciences, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Fujirebio Incorporation, Gilead Sciences, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Springbank Pharmaceuticals, Sysmex Corporation and Roche. J.H. received grants/research support from Roche, Yuhan and Gilead. Y.-O.K. and S.-J.P. have nothing to disclose. J.-W.J. has worked as a local consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb and Gilead Sciences, and received grants/research support from Yuhan, Hanmi and Sysmex Corporation. J.-H.Y. received grants from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Daewoong and Bukwang. Y. Tami, C.F.B. and T.J.K. are employees and stock/shareholders of Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc. S.Y., P.Y., J.C., F.C., R.E., M.P. and D.T. are employees and stock/shareholders of GlaxoSmithKline. Y. Tao is an employee of GlaxoSmithKline.
Figures


Comment in
-
Hepatitis B: a new weapon against an old enemy.Nat Med. 2021 Oct;27(10):1672-1673. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01512-5. Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 34642493 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bepirovirsen assessment in chronic hepatitis B.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Dec;18(12):832. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00547-w. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34725495 No abstract available.
-
Making safe sense of an anti-sense!Cell Rep Med. 2022 Jan 18;3(1):100503. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100503. eCollection 2022 Jan 18. Cell Rep Med. 2022. PMID: 35106512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guidelines for the Prevention, Care and Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection (World Health Organization, 2015); https://www.who.int/hiv/pub/hepatitis/hepatitis-b-guidelines/en/ - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

