Silencing long noncoding RNA LINC01138 inhibits aerobic glycolysis to reduce glioma cell proliferation by regulating the microRNA‑375/SP1 axis
- PMID: 34643249
- PMCID: PMC8524433
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12486
Silencing long noncoding RNA LINC01138 inhibits aerobic glycolysis to reduce glioma cell proliferation by regulating the microRNA‑375/SP1 axis
Abstract
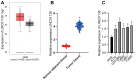
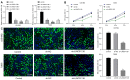
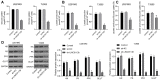
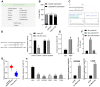
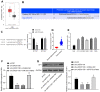
Glioma is a primary cerebral neoplasm that originates from glial tissue and spreads to the central nervous system. Long noncoding RNAs are known to play a role in glioma cells by regulating cell proliferation, migration and invasion. The aim of the present study was to investigate the mechanism by which long intergenic non‑protein coding RNA (LINC) 01138 affects glycolysis and proliferation in glioma cells via the microRNA (miR)‑375/specificity protein 1 (SP1) axis. LINC01138 expression was assessed in glioma tissues and cells using reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR and the association between LINC01138 and patient clinicopathological features was analyzed. Glucose uptake, lactic acid secretion, cell proliferation, and glycolysis‑related enzyme levels were detected following LINC01138 silencing using CCK‑8, EDU assay and western blot analysis. miR‑375 and SP1 expression levels were also assessed, and the distribution of LINC01138 in the nucleus and cytoplasm was investigated using subcellular fractionation localization. Furthermore, the binding relationships between LINC01138 and miR‑375, and between miR‑375 and SP1 were assessed via dual‑luciferase experiment, RIP and RNA pull‑down assays. Finally, xenograft transplantation models were used to verify the in vitro results. LINC01138 was highly expressed in glioma, which was independent of patient sex or age but was significantly related to tumor diameter, the World Health Organization tumor grade and lymph node metastasis. Silencing LINC01138 significantly reduced glioma glycolysis and cell proliferation. Moreover, LINC01138 acted as a competing endogenous RNA to sponge miR‑375 and promote SP1 expression. miR‑375 inhibition significantly reversed the effect of LINC01138 silencing. In addition, silencing LINC01138 significantly reduced tumor growth in vivo. The present study demonstrated that silencing LINC01138 inhibited aerobic glycolysis and thus reduced glioma cell proliferation, potentially by modulating the miR‑375/SP1 axis.
Keywords: competing endogenous RNA; glycolysis; human glioma; long intergenic non‑protein coding RNA 01138; long noncoding RNA; microRNA‑375; proliferation; specificity protein 1; subcellular localization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
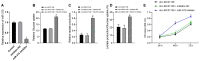

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

