COVID-19 in children: I. Epidemiology, prevention and indirect impacts
- PMID: 34643307
- PMCID: PMC8662210
- DOI: 10.1111/jpc.15791
COVID-19 in children: I. Epidemiology, prevention and indirect impacts
Abstract
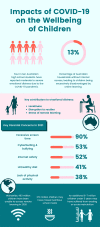
Children globally have been profoundly impacted by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. This review explores the direct and indirect public health impacts of COVID-19 on children. We discuss in detail the transmission dynamics, vaccination strategies and, importantly, the 'shadow pandemic', encompassing underappreciated indirect impacts of the pandemic on children. The indirect effects of COVID-19 will have a long-term impact beyond the immediate pandemic period. These include the mental health and wellbeing risks, disruption to family income and attendant stressors including increased family violence, delayed medical attention and the critical issue of prolonged loss of face-to-face learning in a normal school environment. Amplification of existing inequities and creation of new disadvantage are likely additional sequelae, with children from vulnerable families disproportionately affected. We emphasise the responsibility of paediatricians to advocate on behalf of this vulnerable group to ensure the longer-term effects of COVID-19 public health responses on the health and wellbeing of children are fully considered.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; educational impact; school-based transmission; vaccination.
© 2021 Paediatrics and Child Health Division (The Royal Australasian College of Physicians).
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID‐19: Edition 50. Geneva: WHO; 2021.
-
- Howard‐Jones AR, Kok J. The SARS‐CoV‐2 'perfect storm': From humble betacoronavirus to global pandemic. Microbiol. Aust. 2020; 41: 150–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous