Organoid Models for Infectious Disease
- PMID: 34644153
- PMCID: PMC8887824
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-med-042320-023055
Organoid Models for Infectious Disease
Abstract
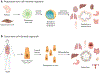
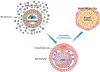
Infectious diseases affect individual health and have widespread societal impacts. New ex vivo models are critical to understand pathogenesis, host response, and features necessary to develop preventive and therapeutic treatments. Pluripotent and tissue stem cell-derived organoids provide new tools for the study of human infections. Organoid models recapitulate many characteristics of in vivo disease and are providing new insights into human respiratory, gastrointestinal, and neuronal host-microbe interactions. Increasing culture complexity by adding the stroma, interorgan communication, and the microbiome will improve the use of organoids as models for infection. Organoid cultures provide a platform with the capability to improve human health related to infectious diseases.
Keywords: infection; organoid; pathogenesis; stem cell; therapies.
Figures
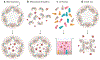
References
LITERATURE CITED
-
- GBD 2016 DALYs and HALE Collab. 2017. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 390(10100):1260–344 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Michaud CM. 2009. Global burden of infectious diseases. Encycl. Microbiol 2009:444–54
-
- Colzani E 2019. Beyond morbidity and mortality: the burden of infectious diseases on healthcare services. Epidemiol. Infect 147:e251
RELATED RESOURCES
-
- Bhatia SN, Ingber DE. 2014. Microfluidic organs-on-chips. Nat. Biotechnol 32(8):760–72 - PubMed
-
- Bar-Ephraim YE, Kretzschmar K, Clevers H. 2020. Organoids in immunological research. Nat. Rev. Immunol 20(5):279–93 - PubMed
-
- Brazovskaja A, Treutlein B, Camp JG. 2019. High-throughput single-cell transcriptomics on organoids. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 55:167–71 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

