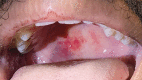
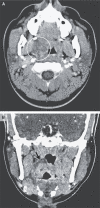
Case 31-2021: A 21-Year-Old Man with Sore Throat, Epistaxis, and Oropharyngeal Petechiae
- PMID: 34644476
- PMCID: PMC8531984
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMcpc2027096
Case 31-2021: A 21-Year-Old Man with Sore Throat, Epistaxis, and Oropharyngeal Petechiae
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
