A mouse-specific retrotransposon drives a conserved Cdk2ap1 isoform essential for development
- PMID: 34644528
- PMCID: PMC8787082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.09.021
A mouse-specific retrotransposon drives a conserved Cdk2ap1 isoform essential for development
Abstract
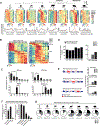
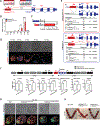
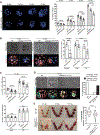
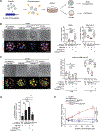
Retrotransposons mediate gene regulation in important developmental and pathological processes. Here, we characterized the transient retrotransposon induction during preimplantation development of eight mammals. Induced retrotransposons exhibit similar preimplantation profiles across species, conferring gene regulatory activities, particularly through long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposon promoters. A mouse-specific MT2B2 retrotransposon promoter generates an N-terminally truncated Cdk2ap1ΔN that peaks in preimplantation embryos and promotes proliferation. In contrast, the canonical Cdk2ap1 peaks in mid-gestation and represses cell proliferation. This MT2B2 promoter, whose deletion abolishes Cdk2ap1ΔN production, reduces cell proliferation and impairs embryo implantation, is developmentally essential. Intriguingly, Cdk2ap1ΔN is evolutionarily conserved in sequence and function yet is driven by different promoters across mammals. The distinct preimplantation Cdk2ap1ΔN expression in each mammalian species correlates with the duration of its preimplantation development. Hence, species-specific transposon promoters can yield evolutionarily conserved, alternative protein isoforms, bestowing them with new functions and species-specific expression to govern essential biological divergence.
Keywords: Cdk2; Cdk2ap1; cell proliferation; implantation; mammals; mouse; preimplantation embryos; promoters; retrotransposons; transposons.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
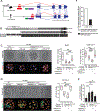
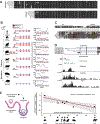
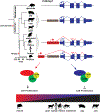
Comment in
-
Retrotransposing a promoter for development.Nat Cell Biol. 2021 Dec;23(12):1221-1223. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00806-7. Nat Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34873284 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 OD027053/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS099761/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG010972/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS120287/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA180996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA200060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS096068/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HD096108/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R25 DA027995/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 ES026699/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA139067/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009391/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG012070/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007175/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 GM114414/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

