Workplace-related inhalation test - Specific inhalation challenge: S2k Guideline of the German Society for Occupational and Environmental Medicine e.V. (DGAUM), the German Society for Pneumology and Respiratory Medicine e.V. (DGP) and the German Society for Allergology and Clinical Immunology e.V. (DGAKI)
- PMID: 34646977
- PMCID: PMC8507414
- DOI: 10.5414/ALX02280E
Workplace-related inhalation test - Specific inhalation challenge: S2k Guideline of the German Society for Occupational and Environmental Medicine e.V. (DGAUM), the German Society for Pneumology and Respiratory Medicine e.V. (DGP) and the German Society for Allergology and Clinical Immunology e.V. (DGAKI)
Abstract
Not available.
Keywords: allergic asthma; allergic sensitization; occupational asthma.
© Dustri-Verlag Dr. K. Feistle.
Figures


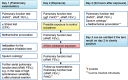
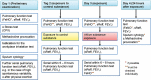
References
-
- Alberts WM Getting the most from the “gold standard”. Chest. 2003; 123: 987–989. - PubMed
-
- D’Alpaos V Vandenplas O Evrard G Jamart J Inhalation challenges with occupational agents: threshold duration of exposure. Respir Med. 2013; 107: 739–744. - PubMed
-
- Baur X Haamann F Heutelbeck A Haeckel R Hallier E Kraus T Merget R Nowak D Triebig G van Kampen V Schneider J Woitowitz HJ Arbeitsmedizinische Leitlinie der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Arbeitsmedizin und Umweltmedizin e.V. (DGAUM). Arbeitsplatzbezogener Inhalationstest (AIT). Arbeitsmed Sozialmed Umweltmed.. 2010; 45: 443–441.
-
- Barbinova L Baur X Increase in exhaled nitric oxide (eNO) after work-related isocyanate exposure. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2006; 79: 387–395. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann KC Kroidl R Liebetrau G Müller-Wening D Sennekamp J Vogelmeier C [Recommendations of the German Society of Pneumology for inhalational provocation testing in exogenous allergic alveolitis. Exogenous-Allergic Alveolitis Study Group of the German Society of Allergology and clinical Immunology and the German Society of Pneumology]. Pneumologie. 1998; 52: 444–446. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
