Novel monkey mAbs induced by a therapeutic vaccine targeting the hepatitis B surface antigen effectively suppress hepatitis B virus in mice
- PMID: 34646979
- PMCID: PMC8499627
- DOI: 10.1093/abt/tbab020
Novel monkey mAbs induced by a therapeutic vaccine targeting the hepatitis B surface antigen effectively suppress hepatitis B virus in mice
Abstract
Background: We have previously obtained a mouse anti-hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) antibody E6F6 with long-lasting serum HBsAg clearance effects. The E6F6 epitope-based protein CR-T3-SEQ13 (HBsAg aa 113-135) vaccination therapy in cynomolgus monkeys induced long-term polyclonal antibodies-mediated clearance of HBsAg in the HBV transgenic (HBV-Tg) mice.
Methods: We isolated monoclonal antibodies from CR-T3-SEQ13 vaccinated cynomolgus monkeys, compared their therapeutic effects with E6F6, identified their epitopes on HBsAg, determined the pharmacokinetics and studied their physical property.
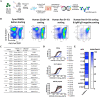
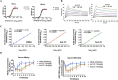
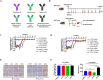
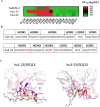
Results: A panel of anti-HBsAg mAbs was generated through memory B cell stimulatory culture. Two lead monkey-human chimeric antibodies, C1-23 and C3-23, effectively suppressed HBsAg and HBV DNA in HBV-Tg mice. The humanized antibodies and humanized-mouse reverse chimeric antibodies of two antibodies exhibited comparable HBsAg clearance and viral suppression efficacy as those versions of E6F6 in HBV-Tg mice. Humanized antibody hu1-23 exhibited more efficacy HBsAg-suppressing effects than huE6F6-1 and hu3-23 in HBV-Tg mice at dose levels of 10 and 20 mg/kg. Evaluation of the binding sites indicates that the epitope recognized by hu1-23 is located in HBsAg aa 118-125 and 121-125 for hu3-23. Physical property study revealed that hu1-23 and hu3-23 are stable enough for further development as a drug candidate.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the CR-T3-SEQ13 protein is a promising HBV therapeutic vaccine candidate, and hu1-23 and hu3-23 are therapeutic candidates for the treatment of chronic hepatitis b. Moreover, the generation of antibodies from the epitope-based vaccinated subjects may be an alternative approach for novel antibody drug discovery.
Keywords: B cell culture; antibody-mediated HBV suppression; chronic hepatitis B infection; cynomolgus monkey antibody; hepatitis B surface antigen.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Antibody Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A unique B cell epitope-based particulate vaccine shows effective suppression of hepatitis B surface antigen in mice.Gut. 2020 Feb;69(2):343-354. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317725. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Gut. 2020. PMID: 30926653 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged suppression of HBV in mice by a novel antibody that targets a unique epitope on hepatitis B surface antigen.Gut. 2016 Apr;65(4):658-71. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308964. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Gut. 2016. PMID: 26423112
-
Antibody-mediated immunotherapy against chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017 Aug 3;13(8):1768-1773. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1319021. Epub 2017 May 19. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017. PMID: 28521640 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine- and hepatitis B immune globulin-induced escape mutations of hepatitis B virus surface antigen.J Biomed Sci. 2001 May-Jun;8(3):237-47. doi: 10.1007/BF02256597. J Biomed Sci. 2001. PMID: 11385295 Review.
-
[Hepatitis B vaccines-history, achievements, challenges, and perspectives].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2022 Feb;65(2):170-182. doi: 10.1007/s00103-021-03484-w. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2022. PMID: 35015108 Free PMC article. Review. German.
Cited by
-
A Dual-domain Engineered Antibody for Efficient HBV Suppression and Immune Responses Restoration.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Apr;11(15):e2305316. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305316. Epub 2024 Feb 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38342604 Free PMC article.
-
HBsAg and TLR7/8 dual-targeting antibody-drug conjugates induce sustained anti-HBV activity in AAV/HBV mice: a preliminary study.Antib Ther. 2024 Jul 3;7(3):249-255. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbae016. eCollection 2024 Jul. Antib Ther. 2024. PMID: 39262443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schweitzer, A, Horn, J, Mikolajczyk, RT et al. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet 2015; 386: 1546–55. - PubMed
-
- Migone, TS, Subramanian, GM, Zhong, J et al. Raxibacumab for the treatment of inhalational anthrax. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 135–44. - PubMed
-
- Malley, R, DeVincenzo, J, Ramilo, O et al. Reduction of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in tracheal aspirates in intubated infants by use of humanized monoclonal antibody to RSV F protein. J Infect Dis 1998; 178: 1555–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
