Fiber-Based Biopolymer Processing as a Route toward Sustainability
- PMID: 34647374
- PMCID: PMC8741650
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202105196
Fiber-Based Biopolymer Processing as a Route toward Sustainability
Abstract
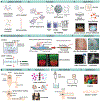
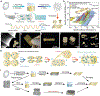
Some of the most abundant biomass on earth is sequestered in fibrous biopolymers like cellulose, chitin, and silk. These types of natural materials offer unique and striking mechanical and functional features that have driven strong interest in their utility for a range of applications, while also matching environmental sustainability needs. However, these material systems are challenging to process in cost-competitive ways to compete with synthetic plastics due to the limited options for thermal processing. This results in the dominance of solution-based processing for fibrous biopolymers, which presents challenges for scaling, cost, and consistency in outcomes. However, new opportunities to utilize thermal processing with these types of biopolymers, as well as fibrillation approaches, can drive renewed opportunities to bridge this gap between synthetic plastic processing and fibrous biopolymers, while also holding sustainability goals as critical to long-term successful outcomes.
Keywords: cellulose; fibrous biopolymers; processing; silk; sustainability; thermal processing.
© 2021 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures









References
-
- Cozzi L, Gould T, International Energy Agency 2015.
-
- Corcoran PL, Environ. Sci.: Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1363. - PubMed
-
- Lau WWY, Shiran Y, Bailey RM, Cook E, Stuchtey MR, Koskella J, Velis CA, Godfrey L, Boucher J, Murphy MB, Thompson RC, Jankowska E, Castillo Castillo A, Pilditch TD, Dixon B, Koerselman L, Kosior E, Favoino E, Gutberlet J, Baulch S, Atreya ME, Fischer D, He KK, Petit MM, Sumaila UR, Neil E, Bernhofen MV, Lawrence K, Palardy JE, Science 2020, 369, 1455. - PubMed
-
- Coates GW, Getzler YDYL, Nat. Rev. Mater 2020, 5, 501.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

