Xanthopsin-Like Systems via Site-Specific Click-Functionalization of a Retinoic Acid Binding Protein
- PMID: 34647400
- PMCID: PMC8934143
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202100449
Xanthopsin-Like Systems via Site-Specific Click-Functionalization of a Retinoic Acid Binding Protein
Abstract
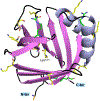
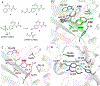
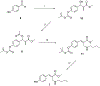
The use of light-responsive proteins to control both living or synthetic cells, is at the core of the expanding fields of optogenetics and synthetic biology. It is thus apparent that a richer reaction toolbox for the preparation of such systems is of fundamental importance. Here, we provide a proof-of-principle demonstration that Morita-Baylis-Hillman adducts can be employed to perform a facile site-specific, irreversible and diastereoselective click-functionalization of a lysine residue buried into a lipophilic binding pocket and yielding an unnatural chromophore with an extended π-system. In doing so we effectively open the path to the in vitro preparation of a library of synthetic proteins structurally reminiscent of xanthopsin eubacterial photoreceptors. We argue that such a library, made of variable unnatural chromophores inserted in an easy-to-mutate and crystallize retinoic acid transporter, significantly expand the scope of the recently introduced rhodopsin mimics as both optogenetic and "lab-on-a-molecule" tools.
Keywords: Morita-Baylis-Hillman adducts; PYP-like chromophores; light-sensitive proteins; site-specific reactions; synthetic xanthopsin-like proteins.
© 2021 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures

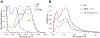

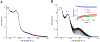
References
-
- Schmidt D, Cho YK, Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 80–91. - PubMed
-
- Stano P, Mavelli F, Life 2015, 5, 1700–1702.
-
- Kandori H, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 2019, 93, 76–85.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

