SARS-CoV-2 Psychiatric Sequelae: A Review of Neuroendocrine Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 34648616
- PMCID: PMC8524640
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyab069
SARS-CoV-2 Psychiatric Sequelae: A Review of Neuroendocrine Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
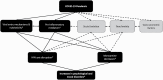
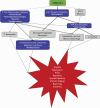
From the earliest days of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, there have been reports of significant neurological and psychological symptoms following Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. This narrative review is designed to examine the potential psychoneuroendocrine pathogenic mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 elicits psychiatric sequelae as well as to posit potential pharmacologic strategies to address and reverse these pathologies. Following a brief overview of neurological and psychological sequelae from previous viral pandemics, we address mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 could enter or otherwise elicit changes in the CNS. We then examine the hypothesis that COVID-19-induced psychiatric disorders result from challenges to the neuroendocrine system, in particular the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal stress axis and monoamine synthesis, physiological mechanisms that are only further enhanced by the pandemic-induced social environment of fear, isolation, and socioeconomic pressure. Finally, we evaluate several FDA-approved therapeutics in the context of COVID-19-induced psychoneuroendocrine disorders.
Keywords: COVID-19; neuroendocrine; neuroimmunology; neuropsychiatric disorders; therapeutic strategies.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures
References
-
- Arısoy O, Bes C, Cifci C, Sercan M, Soy M (2013) The effect of TNF-alpha blockers on psychometric measures in ankylosing spondylitis patients: a preliminary observation. Rheumatol Int 33:1855–1864. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

