Ultrasound-mediated radical cascade reactions: Fast synthesis of functionalized indolines from 2-(((N-aryl)amino)methyl)acrylates
- PMID: 34649162
- PMCID: PMC8517378
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105778
Ultrasound-mediated radical cascade reactions: Fast synthesis of functionalized indolines from 2-(((N-aryl)amino)methyl)acrylates
Abstract
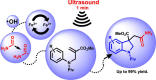
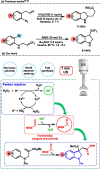
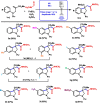
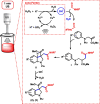
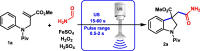
Novel functionalized indolines were synthesized from 2-(((N-aryl)amino)methyl)acrylates and formamides under ultrasonic irradiation for the first time. Aiming to develop a straightforward and easy-to-implement methodology for the synthesis of indolines, an instrumentation setup was designed, including ultrasound (US) equipment (Ultrasonic Horn; tip diameter of 12.7 mm, 20 kHz, maximum power of 400 W), an open reaction flask, and an inexpensive and green catalyst (1 mol%; FeSO4·7H2O; CAS: 7782-63-0) without the need for anhydrous conditions. The use of the sono-Fenton process in the presence of formamides and 2-(((N-aryl)amino)methyl)acrylates afforded a broad range of functionalized indolines within 60 s in high yields. Several experimental parameters of the ultrasound-assisted reaction were evaluated, such as amplitude (40-80%), sonication time (15-60 s), and pulsed ultrasonic irradiation. A 60 s silent reaction did not produce the desired indoline. The optimized conditions for US-mediated reactions allowed the production of functionalized indolines in high isolated yields (up to 99%, 60 s reaction, pulse ration 1 s:1 s, US amplitude 60 %).
Keywords: Functionalized indolines; Indolines; Organic synthesis; Pulsed ultrasound; Sono-Fenton; Ultrasound.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Richards W.T., Loomis A.L. The Chemical Effets Of High Frequency Sound Waves: I. A Preliminary Survey. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1927;49:3086–3100. doi: 10.1021/ja01411a015. - DOI
-
- Chatel G., Varma R.S. Ultrasound and microwave irradiation:contributions of alternative physicochemical activation methods to green chemistry. Green Chem. 2019;21:643–650. doi: 10.1039/C9GC02534K. - DOI
-
- Gadilohar B.L., Pinjari D.V., Shankarling G.S. An Energy Efficient Sonochemical Selective Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohols to Benzaldehydes by Using Bio-TSIL Choline Peroxydisulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016;55:4797–4802. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.6b00731. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

