The incidence of cancer-associated thrombosis is increasing over time
- PMID: 34649273
- PMCID: PMC8753193
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005590
The incidence of cancer-associated thrombosis is increasing over time
Abstract
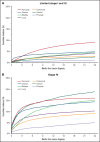
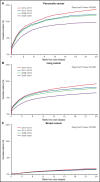
Cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality for patients with malignancy and varies by primary cancer type, stage, and therapy. We aimed to characterize the incidence, risk factors, temporal trends, and the effect on mortality of CAT. The California Cancer Registry was linked to the statewide hospitalization database to identify individuals with the 13 most common malignancies diagnosed between 2005 and 2017 and determine the 6- and 12-month cumulative incidence of CAT by venous thromboembolism (VTE) location, tumor type, and stage after adjusting for competing risk of death. Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to determine risk factors associated with CAT and the effect of CAT on all-cause mortality. 942 019 patients with cancer were identified; 62 003 (6.6%) had an incident diagnosis of CAT. Patients with pancreatic, brain, ovarian, and lung cancer had the highest, and patients with breast and prostate cancer had the lowest 12-month cumulative incidence of CAT. For most malignancies, men, those with metastatic disease and more comorbidities, and African Americans (vs non-Hispanic Whites) were at highest risk for CAT. Patients diagnosed with cancer between 2014 and 2017 had a higher risk of CAT compared with those diagnosed between 2005 and 2007. CAT was associated with increased overall mortality for all malignancies (HR ranges 1.89 to 4.79). The incidence of CAT increased over time and was driven by an increase in pulmonary embolism±deep vein thrombosis (PE±DVT). CAT incidence varies based on tumor type and stage and on individual risk factors including gender, race/ethnicity, and comorbidities. For all tumor types, CAT is associated with an increased mortality.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Chew HK, Wun T, Harvey D, Zhou H, White RH. Incidence of venous thromboembolism and its effect on survival among patients with common cancers. Arch Intern Med. Feb 27 2006;166(4):458-464. - PubMed
-
- Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Kuderer NM, Lyman GH. Frequency, risk factors, and trends for venous thromboembolism among hospitalized cancer patients. Cancer. 2007;110(10):2339-2346. - PubMed
-
- Mulder FI, Horvàth-Puhó E, van Es N, et al. . Venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: a population-based cohort study. Blood. 2021;137(14):1959-1969. - PubMed
-
- Sørensen HT, Mellemkjaer L, Olsen JH, Baron JA. Prognosis of cancers associated with venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(25):1846-1850. - PubMed
-
- Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Kuderer NM, Lyman GH. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(3):632-634. - PubMed

