INCB84344-201: Ponatinib and steroids in frontline therapy for unfit patients with Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 34649276
- PMCID: PMC8941470
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004821
INCB84344-201: Ponatinib and steroids in frontline therapy for unfit patients with Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
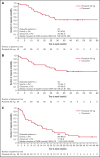
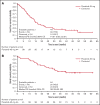
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors have improved survival for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). However, prognosis for old or unfit patients remains poor. In the INCB84344-201 (formerly GIMEMA LAL 1811) prospective, multicenter, phase 2 trial, we tested the efficacy and safety of ponatinib plus prednisone in newly diagnosed patients with Ph+ ALL ≥60 years, or unfit for intensive chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation. Forty-four patients received oral ponatinib 45 mg/d for 48 weeks (core phase), with prednisone tapered to 60 mg/m2/d from days-14-29. Prophylactic intrathecal chemotherapy was administered monthly. Median age was 66.5 years (range, 26-85). The primary endpoint (complete hematologic response [CHR] at 24 weeks) was reached in 38/44 patients (86.4%); complete molecular response (CMR) in 18/44 patients (40.9%) at 24 weeks. 61.4% of patients completed the core phase. As of 24 April 2020, median event-free survival was 14.31 months (95% CI 9.30-22.31). Median overall survival and duration of CHR were not reached; median duration of CMR was 11.6 months. Most common treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were rash (36.4%), asthenia (22.7%), alanine transaminase increase (15.9%), erythema (15.9%), and γ-glutamyltransferase increase (15.9%). Cardiac and vascular TEAEs occurred in 29.5% (grade ≥3, 18.2%) and 27.3% (grade ≥3, 15.9%), respectively. Dose reductions, interruptions, and discontinuations due to TEAEs occurred in 43.2%, 43.2%, and 27.3% of patients, respectively; 5 patients had fatal TEAEs. Ponatinib and prednisone showed efficacy in unfit patients with Ph+ ALL; however, a lower ponatinib dose may be more appropriate in this population. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01641107.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Gleissner B, Gökbuget N, Bartram CR, et al. ; German Multicenter Trials of Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Study Group . Leading prognostic relevance of the BCR-ABL translocation in adult acute B-lineage lymphoblastic leukemia: a prospective study of the German Multicenter Trial Group and confirmed polymerase chain reaction analysis. Blood. 2002;99(5):1536-1543. - PubMed
-
- Faderl S, Kantarjian HM, Thomas DA, et al. . Outcome of Philadelphia chromosome-positive adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000;36(3-4):263-273. - PubMed
-
- Faderl S, Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, Estrov Z. Clinical significance of cytogenetic abnormalities in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1998;91(11):3995-4019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

