Investigating Lipid-Modulating Agents for Prevention or Treatment of COVID-19: JACC State-of-the-Art Review
- PMID: 34649702
- PMCID: PMC8504484
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.08.021
Investigating Lipid-Modulating Agents for Prevention or Treatment of COVID-19: JACC State-of-the-Art Review
Abstract
Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) is associated with systemic inflammation, endothelial activation, and multiorgan manifestations. Lipid-modulating agents may be useful in treating patients with COVID-19. These agents may inhibit viral entry by lipid raft disruption or ameliorate the inflammatory response and endothelial activation. In addition, dyslipidemia with lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and higher triglyceride levels portend worse outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Upon a systematic search, 40 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with lipid-modulating agents were identified, including 17 statin trials, 14 omega-3 fatty acids RCTs, 3 fibrate RCTs, 5 niacin RCTs, and 1 dalcetrapib RCT for the management or prevention of COVID-19. From these 40 RCTs, only 2 have reported preliminary results, and most others are ongoing. This paper summarizes the ongoing or completed RCTs of lipid-modulating agents in COVID-19 and the implications of these trials for patient management.
Keywords: COVID-19; fibrate; lipid-modulating agent; niacin; omega-3; statin.
Copyright © 2021 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding Support and Author Disclosures Dr Gupta received payment from the Arnold & Porter Law Firm for work related to the Sanofi clopidogrel litigation and from the Ben C. Martin Law Firm for work related to an inferior vena cava filter litigation; received consulting fees from Edward Lifesciences; and holds equity in the health care telecardiology startup Heartbeat Health. Dr Madhavan was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute to Columbia University Irving Medical Center (T32 HL007854). Dr Van Tassell has received research support from Novartis, Swedish Orphan Biovitrum, Olatec Therapeutics, and Serpin Pharma; and is a consultant of R-Pharm and Serpin Pharma. Dr Jimenez has served as an advisor or consultant for Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, ROVI, and Sanofi; has served as a speaker or a member of a speaker bureau for Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Leo Pharma, ROVI, and Sanofi; and has received grants for clinical research from Daiichi-Sankyo, Sanofi, and ROVI. Dr Monreal has served as an advisor or consultant for Sanofi, Leo Pharma, and Daiichi-Sankyo; and has received a nonrestricted educational grant by Sanofi and Bayer to sponsor the Computerized Registry of Patients with Venous Thromboembolism. Dr Vaduganathan has received research grant support or served on advisory boards for American Regent, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer AG, Baxter Healthcare, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytokinetics, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, and Relypsa; participates in speaker engagements with Novartis and Roche Diagnostics; and participates on clinical endpoint committees for studies sponsored by Galmed, Novartis, and the National Institutes of Health. Dr Fanikos has served as a consultant for Portola, Inc and Pfizer, Inc. Dr Piazza has received research grant support from BSC, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, Portola, Amgen, and Janssen; and has received consulting fees from Amgen, Pfizer, and BSC. Dr Parikh has served as a noncompensated advisor to Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Cardiovascular Systems Inc, Cordis, Janssen, Medtronic, and Philips; receives institutional research support from Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, SurModics, TriReme, and Veryan Medical; and is a consultant to Abiomed, Inari Medical, Penumbra, and Terumo. Dr Bhatt has served on the advisory board for Cardax, CellProthera, Cereno Scientific, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, Janssen, Level Ex, Medscape Cardiology, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, and Regado Biosciences; has served on the Board of Directors for the Boston VA Research Institute, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, and ToBeSoft; serves as Chair of the American Heart Association Quality Oversight Committee; has served on the data monitoring committees for Baim Institute for Clinical Research (formerly Harvard Clinical Research Institute, the PORTICO trial, funded by St. Jude Medical, now Abbott), Cleveland Clinic (including for the ExCEED trial, funded by Edwards), Contego Medical (Chair, PERFORMANCE 2), Duke Clinical Research Institute, Mayo Clinic, Mount Sinai School of Medicine (for the ENVISAGE trial, funded by Daiichi-Sankyo), Population Health Research Institute; has received honoraria from the American College of Cardiology (Senior Associate Editor, Clinical Trials and News, ACC.org; Vice-Chair, ACC Accreditation Committee), Baim Institute for Clinical Research (formerly Harvard Clinical Research Institute; RE-DUAL PCI clinical trial steering committee funded by Boehringer Ingelheim; AEGIS-II executive committee funded by CSL Behring), Belvoir Publications (Editor in Chief, Harvard Heart Letter), Canadian Medical and Surgical Knowledge Translation Research Group (clinical trial steering committees), Duke Clinical Research Institute (clinical trial steering committees, including for the PRONOUNCE trial, funded by Ferring Pharmaceuticals), HMP Global (Editor in Chief, Journal of Invasive Cardiology), Journal of the American College of Cardiology (Guest Editor; Associate Editor), K2P (Co-Chair, interdisciplinary curriculum), Level Ex, Medtelligence/ReachMD (CME steering committees), MJH Life Sciences, Population Health Research Institute (for the COMPASS operations committee, publications committee, steering committee, and USA national co-leader, funded by Bayer), Slack Publications (Chief Medical Editor, Cardiology Today’s Intervention), Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care (Secretary/Treasurer), WebMD (CME steering committees); other, Clinical Cardiology (Deputy Editor), NCDR-ACTION Registry Steering Committee (Chair), VA CART Research and Publications Committee (Chair); has received research funding from Abbott, Afimmune, Amarin, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cardax, Chiesi, CSL Behring, Eisai, Ethicon, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Forest Laboratories, Fractyl, HLS Therapeutics, Idorsia, Ironwood, Ischemix, Janssen, Lexicon, Lilly, Medtronic, MyoKardia, Novo Nordisk, Owkin, Pfizer, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Synaptic, and The Medicines Company; has received royalties from Elsevier (Editor, Cardiovascular Intervention: A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease); has been a site co-investigator, Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, CSI, St. Jude Medical (now Abbott), and Svelte; has been a trustee for the American College of Cardiology; and has received unfunded research from FlowCo, Merck, and Takeda. Dr Lip is a consultant and speaker for BMS/Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Daiichi-Sankyo (no fees are received personally). Dr Stone has received speaker or other honoraria from Cook, Terumo, and Orchestra Biomed; has been a consultant to Valfix, TherOx, Vascular Dynamics, Robocath, HeartFlow, Gore, Ablative Solutions, Miracor, Neovasc, V-Wave, Abiomed, Ancora, MAIA Pharmaceuticals, Vectorious, Reva, Matrizyme, and CardioMech; and has equity/options from Ancora, Cagent, Applied Therapeutics, BioStar family of funds, SpectraWave, Orchestra Biomed, Aria, Cardiac Success, Med Focus family of funds, and Valfix. Dr Krumholz has received personal fees from UnitedHealth, IBM Watson Health, Element Science, Aetna, Facebook, Siegfried & Jensen Law Firm, Arnold & Porter Law Firm, Ben C. Martin Law Firm, and the National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases (Beijing, China); has ownership in Hugo Health and Refactor Health; has contracts from the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services; and has received grants from Medtronic, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, and the Shenzhen Center for Health Information, outside the submitted work. Dr Libby is an unpaid consultant to, or involved in clinical trials for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Beren, Esperion Therapeutics, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Kowa Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Regeneron, and XBiotech, Inc; and is a member of the scientific advisory board for Amgen, Corvidia Therapeutics, CSL Behring, DalCor Pharmaceuticals, Genentech, Kowa Pharmaceuticals, Olatec Therapeutics, PlaqueTec, Kancera, Medimmune, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and XBiotech, Inc. Dr Libby is on the Board of Directors of XBiotech, Inc; and has a financial interest in XBiotech, a company developing therapeutic human antibodies. Dr Libby's interests were reviewed and are managed by Brigham and Women's Hospital and Partners HealthCare in accordance with their conflict of interest policies. Dr Libby’s laboratory has received research funding in the last 2 years from Novartis. Dr Goldhaber has received research support from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boston Scientific, Daiichi-Sankyo, Janssen, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and the Thrombosis Research Institute; and has received consulting fees from Bayer, Agile, Boston Scientific, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr Bikdeli is a consulting expert, on behalf of the plaintiff, for litigation related to 2 specific brand models of inferior vena cava filters. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
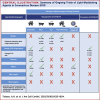


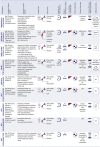



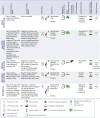
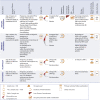
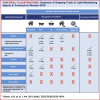
Update of
-
Lipid-Modulating Agents for Prevention or Treatment of COVID-19 in Randomized Trials.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 May 4:2021.05.03.21256468. doi: 10.1101/2021.05.03.21256468. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 Oct 19;78(16):1635-1654. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.08.021. PMID: 33972948 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

