Effect of Delta variant on viral burden and vaccine effectiveness against new SARS-CoV-2 infections in the UK
- PMID: 34650248
- PMCID: PMC8674129
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01548-7
Effect of Delta variant on viral burden and vaccine effectiveness against new SARS-CoV-2 infections in the UK
Abstract
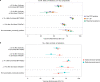
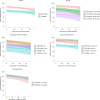
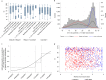
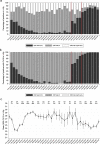
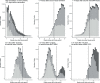
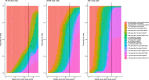
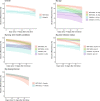
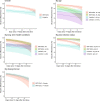
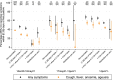
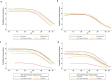
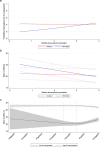
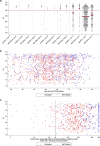
The effectiveness of the BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 vaccines against new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections requires continuous re-evaluation, given the increasingly dominant B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant. In this study, we investigated the effectiveness of these vaccines in a large, community-based survey of randomly selected households across the United Kingdom. We found that the effectiveness of BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 against infections (new polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-positive cases) with symptoms or high viral burden is reduced with the B.1.617.2 variant (absolute difference of 10-13% for BNT162b2 and 16% for ChAdOx1) compared to the B.1.1.7 (Alpha) variant. The effectiveness of two doses remains at least as great as protection afforded by prior natural infection. The dynamics of immunity after second doses differed significantly between BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1, with greater initial effectiveness against new PCR-positive cases but faster declines in protection against high viral burden and symptomatic infection with BNT162b2. There was no evidence that effectiveness varied by dosing interval, but protection was higher in vaccinated individuals after a prior infection and in younger adults. With B.1.617.2, infections occurring after two vaccinations had similar peak viral burden as those in unvaccinated individuals. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination still reduces new infections, but effectiveness and attenuation of peak viral burden are reduced with B.1.617.2.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors uniform disclosure form at
Figures
References
-
- Imai, N. et al. Interpreting estimates of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine efficacy and effectiveness to inform simulation studies of vaccine impact: a systematic review. Wellcome Open Res. 6, 185 https://wellcomeopenresearch.org/articles/6-185 (2021)
-
- Thompson MG, et al. Interim estimates of vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccines in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among health care personnel, first responders, and other essential and frontline workers—eight U.S. locations, December 2020–March 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2021;70:495–500. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7013e3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

