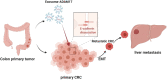
Exosome-Derived ADAM17 Promotes Liver Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 34650435
- PMCID: PMC8506248
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.734351
Exosome-Derived ADAM17 Promotes Liver Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
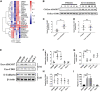
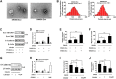
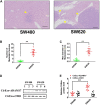
Exosomes derived from cancer cells are deemed important drivers of pre-metastatic niche formation at distant organs, but the underlying mechanisms of their effects remain largely unknow. Although the role of ADAM17 in cancer cells has been well studied, the secreted ADAM17 effects transported via exosomes are less understood. Herein, we show that the level of exosome-derived ADAM17 is elevated in the serum of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer as well as in metastatic colorectal cancer cells. Furthermore, exosomal ADAM17 was shown to promote the migratory ability of colorectal cancer cells by cleaving the E-cadherin junction. Moreover, exosomal ADAM17 overexpression as well as RNA interference results highlighted its function as a tumor metastasis-promoting factor in colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, our current work suggests that exosomal ADAM17 is involved in pre-metastatic niche formation and may be utilized as a blood-based biomarker of colorectal cancer metastasis.
Keywords: ADAM17; E-cadherin; colorectal cancer; exosome; liver metastasis.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Lu, Fu, Lu, Gu, Xu, Dai, Yang and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chafe S. C., Lou Y., Sceneay J., Vallejo M., Hamilton M. J., McDonald P. C., et al. (2015). Carbonic Anhydrase IX Promotes Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Mobilization and Establishment of a Metastatic Niche by Stimulating G-CSF Production. Cancer Res. 75 (6), 996–1008. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3000 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

