Genistein Inhibits the Pathogenesis of Aeromonas hydrophila by Disrupting Quorum Sensing Mediated Biofilm Formation and Aerolysin Production
- PMID: 34650438
- PMCID: PMC8505762
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.753581
Genistein Inhibits the Pathogenesis of Aeromonas hydrophila by Disrupting Quorum Sensing Mediated Biofilm Formation and Aerolysin Production
Abstract
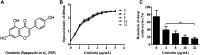
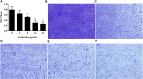
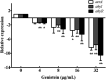
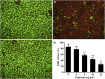
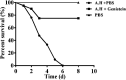
Aeromonas hydrophila is an opportunistic pathogen that is responsible for a variety of infectious diseases both in human and animals, particularly aquatic animals. Moreover, the pathogen has become a foodborne pathogen by transmitting from seafood to human. The abuse of antibiotics in aquaculture results in the emergence of antibiotic resistance and treatment failure. Therefore, novel approaches are urgently needed for managing resistant A. hydrophila associated infections. Aerolysin, an essential virulence factor of pathogenic A. hydrophila strain, has been identified as target developing novel drugs against pathogenesis of A. hydrophila. In the present study, genistein, without anti-A. hydrophila activity, was identified that could decrease the production of aerolysin and biofilm formation at a dose-dependent manner. Transcription of aerolysin encoding gene aerA and quorum sensing related genes ahyI and ahyR was significantly down-regulated when co-cultured with genistein. Cell viability studies demonstrated that genistein could significantly improve aerolysin mediated A549 cell injury. Furthermore, genistein could provide a remarkable protection to channel catfish infected with A. hydrophila. These findings indicate that targeting quorum sensing and virulence can be a useful approach developing drugs against A. hydrophila infections in aquaculture. Moreover, genistein can be chosen as a promising candidate in developing drugs against A. hydrophila.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila; anti-virulence; genistein; natural compound; quorum sensing.
Copyright © 2021 Dong, Zhang, Li, Liu, Zhou, Yang, Xu, Yang and Ai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chakraborty T., Huhle B., Hof H., Bergbauer H., Goebel W. (1987). Marker Exchange Mutagenesis of the Aerolysin Determinant in Aeromonas Hydrophila Demonstrates the Role of Aerolysin in A. Hydrophila-Associated Systemic Infections. Infect. Immun. 55 (9), 2274–2280. 10.1128/iai.55.9.2274-2280.1987 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- CLSI (2009). Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically-Eighth Edition: Approved Standard M07-A8. Wayne, PA, USA: CLSI.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

