ORF3a Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Inhibits Interferon-Activated Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription Signaling via Elevating Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1
- PMID: 34650546
- PMCID: PMC8506155
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.752597
ORF3a Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Inhibits Interferon-Activated Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription Signaling via Elevating Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1
Abstract
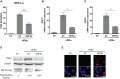
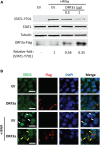
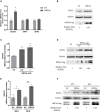
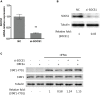
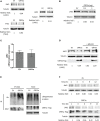
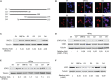
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused a crisis to global public health since its outbreak at the end of 2019. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the pathogen of COVID-19, appears to efficiently evade the host immune responses, including interferon (IFN) signaling. Several SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins are believed to involve in the inhibition of IFN signaling. In this study, we discovered that ORF3a, an accessory protein of SARS-CoV-2, inhibited IFN-activated Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling via upregulating suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1), a negative regulator of cytokine signaling. ORF3a induced SOCS1 elevation in a dose- and time-dependent manner. RNAi-mediated silencing of SOCS1 efficiently abolished ORF3a-induced blockage of JAK/STAT signaling. Interestingly, we found that ORF3a also promoted the ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation of Janus kinase 2 (JAK2), an important kinase in IFN signaling. Silencing of SOCS1 by siRNA distinctly blocked ORF3a-induced JAK2 ubiquitination and degradation. These results demonstrate that ORF3a dampens IFN signaling via upregulating SOCS1, which suppressed STAT1 phosphorylation and accelerated JAK2 ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation. Furthermore, analysis of ORF3a deletion constructs showed that the middle domain of ORF3a (amino acids 70-130) was responsible for SOCS1 upregulation. These findings contribute to our understanding of the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 antagonizing host antiviral response.
Keywords: JAK/STAT signaling; Janus kinase 2 (JAK2); SARS-CoV-2; SOCS1; accessory protein ORF3a; ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Yang, Chang, Xue, Wang, Bai, Zhao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computationally predicted SARS-COV-2 encoded microRNAs target NFKB, JAK/STAT and TGFB signaling pathways.Gene Rep. 2021 Mar;22:101012. doi: 10.1016/j.genrep.2020.101012. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Gene Rep. 2021. PMID: 33398248 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the IFN-α JAK/STAT Pathway by MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-1 Proteins in Human Epithelial Cells.Viruses. 2022 Mar 23;14(4):667. doi: 10.3390/v14040667. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458397 Free PMC article.
-
Type III Interferon Induces Distinct SOCS1 Expression Pattern that Contributes to Delayed but Prolonged Activation of Jak/STAT Signaling Pathway: Implications for Treatment Non-Response in HCV Patients.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 20;10(7):e0133800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133800. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26193702 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS, Intrinsic Virulence Factors, and Treatment of COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 23;11:582102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.582102. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Janus kinase signaling as risk factor and therapeutic target for severe SARS-CoV-2 infection.Eur J Immunol. 2021 May;51(5):1071-1075. doi: 10.1002/eji.202149173. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Eur J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33675065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impairment of antiviral immune response and disruption of cellular functions by SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a and ORF7b.iScience. 2022 Nov 18;25(11):105444. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105444. Epub 2022 Oct 25. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36310646 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Detection of RIG-1, MDA5, and IFIT-1 Expression Is a Convenient Tool for Evaluation of the Interferon-Mediated Response.Viruses. 2022 Sep 21;14(10):2090. doi: 10.3390/v14102090. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36298646 Free PMC article.
-
One gene to rule them all - clinical perspectives of a potent suppressor of cytokine signaling - SOCS1.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 22;15:1385190. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1385190. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38711523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Individual and Synergistic Anti-Coronavirus Activities of SOCS1/3 Antagonist and Interferon α1 Peptides.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 21;13:902956. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.902956. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35799776 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a Protein Impedes Type I Interferon-Activated JAK/STAT Signaling by Interacting with HNRNPA2B1.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 10;26(12):5536. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125536. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565000 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

