Human Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Primed by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interferon-γ Modulate the Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells of Type 1 Diabetic Patients
- PMID: 34650558
- PMCID: PMC8506215
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732549
Human Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Primed by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interferon-γ Modulate the Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells of Type 1 Diabetic Patients
Abstract
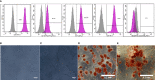
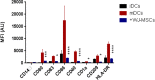
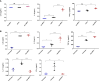
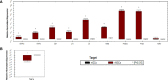
The unique immunomodulation and immunosuppressive potential of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (WJ-MSCs) make them a promising therapeutic approach for autoimmune diseases including type 1 diabetes (T1D). The immunomodulatory effect of MSCs is exerted either by cell-cell contact or by secretome secretion. Cell-cell contact is a critical mechanism by which MSCs regulate immune-responses and generate immune regulatory cells such as tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDCs) and regulatory T cell (Tregs). In this study, we primed WJ-MSCs with TNF-α and IFN-γ and investigated the immunomodulatory properties of primed WJ-MSCs on mature dendritic cells (mDCs) and activated T cells differentiated from mononuclear cells (MNCs) of T1D patient's. Our findings revealed that primed WJ-MSCs impaired the antigen-mediated immunity, upregulated immune-tolerance genes and downregulated immune-response genes. We also found an increase in the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines and suppression of the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Significant upregulation of FOXP3, IL10 and TGFB1 augmented an immunosuppressive effect on adaptive T cell immunity which represented a strong evidence in support of the formation of Tregs. Furthermore, upregulation of many critical genes involved in the immune-tolerance mechanism (IDO1 and PTGES2/PTGS) was detected. Interestingly, upregulation of ENTPD1/NT5E genes express a strong evidence to switch immunostimulatory response toward immunoregulatory response. We conclude that WJ-MSCs primed by TNF-α and IFN-γ may represent a promising tool to treat the autoimmune disorders and can provide a new evidence to consider MSCs- based therapeutic approach for the treatment of TID.
Keywords: Immunomodulation; Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells; priming; regulatory T cells; tolerogenic dendritic cells; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2021 Mrahleh, Matar, Jafar, Wehaibi, Aslam and Awidi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of cytokine licensing in shaping the therapeutic potential of wharton's jelly MSCs: metabolic shift towards immunomodulation at the expense of differentiation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Apr 20;16(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04309-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40254602 Free PMC article.
-
Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Human Umbilical Cord: a Close-up on Immunomodulatory Molecules Featured In Situ and In Vitro.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019 Dec;15(6):900-918. doi: 10.1007/s12015-019-09907-1. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019. PMID: 31741193
-
Decoding Cytokine Dynamics: Wharton's Jelly Stromal Cells and Chondro-Differentiates in PHA-Stimulated Co-Culture.Cells. 2025 Jan 23;14(3):174. doi: 10.3390/cells14030174. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39936966 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and clinical applications of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.Curr Res Transl Med. 2020 Jan;68(1):5-16. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 31543433 Review.
-
Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as a Feeder Layer for the Ex Vivo Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells: a Review.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017 Feb;13(1):35-49. doi: 10.1007/s12015-016-9702-4. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017. PMID: 27853939 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Interferon-Gamma and Hypoxia-Primed Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles: Underlying Mechanisms and Potentials in Clinical Translation.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 20;12(6):1369. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061369. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wogonin preconditioning of MSCs improved their therapeutic efficiency for colitis through promoting glycolysis.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Aug;32(4):2575-2587. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01491-2. Epub 2024 May 16. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38753221
-
Human mesenchymal stem/stromal cell based-therapy in diabetes mellitus: experimental and clinical perspectives.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Oct 29;15(1):384. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03974-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39468609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HLA-G and CD152 Expression Levels Encourage the Use of Umbilical Cord Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as an Alternative for Immunosuppressive Therapy.Cells. 2022 Apr 14;11(8):1339. doi: 10.3390/cells11081339. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35456019 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular systems architecture of the mesenchymal stromal cell microenvironment.Stem Cells. 2025 Aug 22;43(9):sxaf042. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxaf042. Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40843515 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

