Baicalein pre-treatment alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice by regulating the Nrf2/ARE pathway
- PMID: 34650628
- PMCID: PMC8506949
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10816
Baicalein pre-treatment alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice by regulating the Nrf2/ARE pathway
Abstract
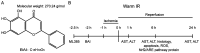
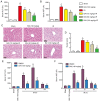
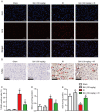
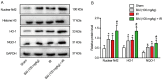
Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI) is caused by blood flow recovery following ischemia. Baicalein (BAI), a natural antioxidant used in traditional Chinese medicine, eliminates excessive free radicals and protects the structure of the cell membrane. However, its protective mechanism against HIRI is still unclear. The present study investigated underlying mechanism using a mouse HIRI model. Liver injury was evaluated using serum levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, and hematoxylin-eosin staining was performed to evaluate the pathological changes in liver tissue. Apoptosis of hepatocytes was detected by TUNEL staining. The expression levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the liver were detected to evaluate oxidative stress. Western blotting was performed to assess expression levels of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/antioxidant response elements (ARE) pathway proteins in liver tissue. BAI pre-treatment significantly decreased elevation of serum aminotransferase levels induced by IR and alleviated histological damage to the liver. BAI decreased production of ROS and MDA in liver tissue induced by IR and increased the activity of SOD. At the same time, BAI inhibited apoptosis of liver cells induced by oxidative stress. Furthermore, BAI promoted the translocation of Nrf2 into the nucleus and increased the expression of total heme oxygenase-1 and NAD(P)H dehydrogenase quinone-1. The Nrf2 inhibitor ML385 reversed the protective effect of BAI on HIRI. These results indicated that BAI served a protective effect in HIRI by regulating the Nrf2/ARE pathway.
Keywords: baicalein; hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury; nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 signaling; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright: © Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dexmedetomidine alleviates ferroptosis following hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by upregulating Nrf2/GPx4-dependent antioxidant responses.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec 31;169:115915. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115915. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 38000361
-
Sulforaphane reduces apoptosis and oncosis along with protecting liver injury-induced ischemic reperfusion by activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway.Hepatol Int. 2015 Apr;9(2):321-9. doi: 10.1007/s12072-014-9604-y. Epub 2015 Jan 25. Hepatol Int. 2015. PMID: 25788192
-
MCTR1 inhibits ferroptosis by promoting NRF2 expression to attenuate hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022 Sep 1;323(3):G283-G293. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00354.2021. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35916424
-
Research progress of nano selenium in the treatment of oxidative stress injury during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 4;13:1103483. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1103483. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36686647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New progress in understanding roles of nitric oxide during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.World J Hepatol. 2022 Mar 27;14(3):504-515. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.504. World J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35582289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis In Vivo and In Vitro.Inflammation. 2023 Jun;46(3):1061-1076. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01792-8. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 36856879 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Pyroptosis and Autophagy in Ischemia Reperfusion Injury.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 21;12(7):1010. doi: 10.3390/biom12071010. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detoxification technology and mechanism of processing with Angelicae sinensis radix in reducing the hepatotoxicity induced by rhizoma Dioscoreae bulbiferae in vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 28;13:984858. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.984858. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36249801 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalein improves the chemoresistance of ovarian cancer through regulation of CirSLC7A6.J Ovarian Res. 2023 Nov 8;16(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01285-0. J Ovarian Res. 2023. PMID: 37940982 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2-mediated therapeutic effects of dietary flavones in different diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 12;14:1240433. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1240433. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37767395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
