Value of the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting COVID-19 Severity: A Meta-analysis
- PMID: 34650648
- PMCID: PMC8510823
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2571912
Value of the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting COVID-19 Severity: A Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is highly contagious and continues to spread rapidly. However, there are no simple and timely laboratory techniques to determine the severity of COVID-19. In this meta-analysis, we assessed the potential of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as an indicator of severe versus nonsevere COVID-19 cases.
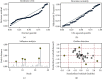
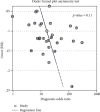
Methods: A search for studies on the NLR in severe and nonsevere COVID-19 cases published from January 1, 2020, to July 1, 2021, was conducted on the PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library databases. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under the curve (AUC) analyses were done on Stata 14.0 and Meta-disc 1.4 to assess the performance of the NLR.
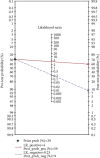
Results: Thirty studies, including 5570 patients, were analyzed. Of these, 1603 and 3967 patients had severe and nonsevere COVID-19, respectively. The overall sensitivity and specificity were 0.82 (95% confidence interval (CI), 0.77-0.87) and 0.77 (95% CI, 0.70-0.83), respectively; positive and negative correlation ratios were 3.6 (95% CI, 2.7-4.7) and 0.23 (95% CI, 0.17-0.30), respectively; DOR was 16 (95% CI, 10-24), and the AUC was 0.87 (95% CI, 0.84-0.90).
Conclusion: The NLR could accurately determine the severity of COVID-19 and can be used to identify patients with severe disease to guide clinical decision-making.
Copyright © 2021 Ying Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest declared.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Value of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio for Predicting the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis.Dis Markers. 2020 Apr 27;2020:9731854. doi: 10.1155/2020/9731854. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 32454909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive values of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on disease severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2020 Nov 16;24(1):647. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03374-8. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 33198786 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of SARS-CoV-2 patients identifies the combinatorial significance of D-dimer, C-reactive protein, lymphocyte, and neutrophil values as a predictor of disease severity.Int J Lab Hematol. 2021 Apr;43(2):324-328. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13354. Epub 2020 Oct 3. Int J Lab Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33010111 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, a critical predictor for assessment of disease severity in patients with COVID-19.Int J Lab Hematol. 2021 Apr;43(2):329-335. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13374. Epub 2020 Oct 25. Int J Lab Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33099889
-
The neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is an independent predictor for severe COVID-19 : Evidence from a multicenter case-control study and meta-analyses.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2021 Sep;133(17-18):882-891. doi: 10.1007/s00508-021-01917-9. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2021. PMID: 34342712 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A two-gene marker for the two-tiered innate immune response in COVID-19 patients.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 17;18(1):e0280392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280392. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36649304 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Characteristics of Patients for Hospitalized Severe COVID-19 Infected by the Omicron Variants and Wild Type of SARS-CoV-2 in China.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Jul 21;16:3063-3078. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S420721. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37497065 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicting Case Severity in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Review.Cureus. 2022 Sep 29;14(9):e29760. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29760. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36187170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive Value of Systemic Immune-Inflammation index and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Severe COVID-19.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2022 Jan-Dec;28:10760296221111391. doi: 10.1177/10760296221111391. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2022. PMID: 35765218 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent immune responses in COVID-19-mediated liver injury: focus on cytokines.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 15;14:1139692. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1139692. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37654571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Craig D. G., Kitto L., Zafar S., et al. An elevated neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio is associated with adverse outcomes following single time-point paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose: a time-course analysis. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology . 2014;26(9):1022–1029. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000157. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

