ZLN005 protects against ischemia-reperfusion-induced kidney injury by mitigating oxidative stress through the restoration of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation
- PMID: 34650679
- PMCID: PMC8507071
ZLN005 protects against ischemia-reperfusion-induced kidney injury by mitigating oxidative stress through the restoration of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation
Abstract
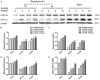
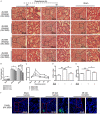
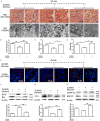
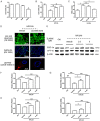
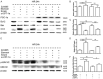
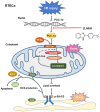
To date, the treatment of acute kidney injury (AKI) remains a difficult problem for clinicians. In the present study, we assessed whether ZLN005, a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) agonist, can protect against ischemic AKI in vivo and in vitro. Notably, ZLN005 treatment significantly alleviated Ischemia-reperfusion (I/R)-induced tubular injury and reversed the decrease in hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced cell viability by restoring PGC-1α expression in a dose-dependent manner. This beneficial effect of ZLN005 was associated with the preservation of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (MitoFAO) and the alleviation of oxidative stress. Cotreatment with etomoxir, a specific inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1α (CPT-1α) activity, or CPT-1α siRNA abrogated ZLN005-induced antistress responses by mitigating reactive oxygen species production and decreasing apoptosis under ischemia-hypoxia conditions by suppressing MitoFAO. Further studies revealed that activation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress may be involved in the effect of CPT-1α inhibition observed in vivo and in vitro. Collectively, our results suggest that ZLN005 confers a protective effect on I/R-induced kidney injury by mitigating ER stress through the restoration of MitoFAO by targeting PGC-1α.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; ZLN005; apoptosis; carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1α; oxidative stress; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet. 2012;380:756–766. - PubMed
-
- Liao W, Fu Z, Zou Y, Wen D, Ma H, Zhou F, Chen Y, Zhang M, Zhang W. MicroRNA-140-5p attenuated oxidative stress in cisplatin induced acute kidney injury by activating Nrf2/ARE pathway through a Keap1-independent mechanism. Exp Cell Res. 2017;360:292–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
