The correlation of the miR-29a/MMP9 axis with Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancer
- PMID: 34650687
- PMCID: PMC8506987
The correlation of the miR-29a/MMP9 axis with Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancer
Abstract
Objective: This study was designed to investigate the association between the miR-29a/MMP9 axis expression levels and Helicobacter pylori (HP) infection in gastric cancer patients.
Methods: A total of 100 gastric cancer patients referred to our hospital from June 2017 to June 2019 were recruited as the study cohort. Among them, 50 HP-positive patients were included in the experimental group and 50 HP-negative patients were included in the control group. The changes in the patients' conditions were compared, the miR-29a/MMP9 axis expression levels were recorded, and the correlation between the miR-29a/MMP9 axis and the HP infections was analyzed. All the discharged patients were followed up for one year to analyze the correlation between the HP infections and the serum miR-29a and MMP9 expression levels with the disease progression.
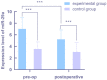
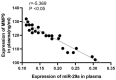
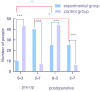
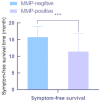
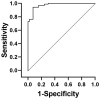
Results: The experimental group had higher miR-29a expression levels and higher MMP9 chromogenic scores than the control group (P<0.05). A negative correlation was found between the miR-29 expression level and the MMP9 expression level (r=-5.369, P<0.05). One year after discharge, there were 27 patients with severe disease in the experimental group and 6 in the control group, with a significant difference between the two groups. Moreover, the expression levels of the miR-29a/MMP9 axis were significantly higher in the discharged patients than in the patients with severe disease (P<0.05). A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyze the predictive value of miR-29/MMP9 in the diagnosis of gastric cancer, and the area under the curve was found to be 0.97.
Conclusion: The miR-29a/MMP9 axis levels were increased in the HP positive patients but not in the HP negative patients. HP infection is considered to be closely related to gastric cancer cell spread, disease relapse, and high miR-29a/MMP9 axis expression levels.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; gastric cancer; miR-29a/MMP9 axis.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Yang J, Liu Z, Zeng B, Hu G, Gan R. Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer: a distinct subtype. Cancer Lett. 2020;495:191–199. - PubMed
-
- Yan Y, Fang L, Li Y, Yu Y, Li Y, Cheng JC, Sun YP. Association of MMP2 and MMP9 gene polymorphisms with the recurrent spontaneous abortion: a meta-analysis. Gene. 2021;767:145173. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Xu XY, Shen Y, Ye CF, Hu N, Yao Q, Lv XZ, Long SL, Ren C, Lang YY, Liu YL. Ghrelin protects against obesity-induced myocardial injury by regulating the lncRNA H19/miR-29a/IGF-1 signalling axis. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020;114:104405. - PubMed
-
- Xu G, Wei J, Huangfu B, Gao J, Wang X, Xiao L, Xuan R, Chen Z, Song G. Animal model and bioinformatics analyses suggest the TIMP1/MMP9 axis as a potential biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2020;59:1302–1316. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
