Low-molecular-weight heparin reduces the formation of lower limb deep venous thrombosis in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage
- PMID: 34650721
- PMCID: PMC8507008
Low-molecular-weight heparin reduces the formation of lower limb deep venous thrombosis in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage
Abstract
Objective: To demonstrate that low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) can reduce the formation of lower limb deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and improve the quality of life (QOL) of patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage (HICH).
Methods: Totally, 98 patients with HICH were selected according to different treatment and intervention schemes. Patients receiving routine intracranial pressure reduction and blood pressure regulation intervention were included in group A (n=46) and those receiving LMWH calcium on the basis of treatment in group A were included in group B (n=52). The total effective rate of patients was compared between the two groups, and the prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), fibrinogen degradation product (FDP), D-dimer, and inflammatory factor levels as well as complications and QOL scores before and after treatment were recorded and compared.
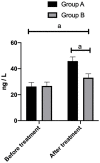
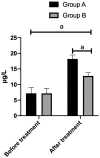
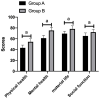
Results: The FDP and D-dimer showed an increasing trend in both groups after treatment, with the increase being significantly lower in group B than in group A (P<0.001). Serum tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β levels increased significantly in the two groups after treatment, with the increase being significantly lower in group B than in group A (P<0.05). Complications of pulmonary embolism, DVT, intracranial hemorrhage, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage were better in group B than in group A (P<0.05). In terms of QOL, physical and mental health, material life, and social functioning were significantly higher in patients of group B than for those in group A (P<0.001).
Conclusions: The application of LMWH in patients with HICH can reduce the formation of lower limb DVT.
Keywords: Low-molecular-weight heparin; hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage; lower limb deep venous thrombosis; quality of life.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preventive effects of low molecular weight heparin on formation of deep vein thrombosis by reducing D dimer values in patients undergoing spinal surgery.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Jan;22(1):229-237. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201801_14122. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29364491
-
A fixed-dose combination of low molecular weight heparin with dihydroergotamine versus adjusted-dose unfractionated heparin in the prevention of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip replacement.Thromb Haemost. 1996 Feb;75(2):246-50. Thromb Haemost. 1996. PMID: 8815569 Clinical Trial.
-
Prevention of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage.Neurologist. 2009 Nov;15(6):329-31. doi: 10.1097/NRL.0b013e3181a93bac. Neurologist. 2009. PMID: 19901711 Clinical Trial.
-
Deep vein thrombosis: update on diagnosis and management.Med J Aust. 2019 Jun;210(11):516-524. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50201. Epub 2019 Jun 2. Med J Aust. 2019. PMID: 31155730 Review.
-
What is the optimal pharmacological prophylaxis for the prevention of deep-vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients with acute ischemic stroke?Thromb Res. 2007;119(3):265-74. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2006.03.010. Epub 2006 May 3. Thromb Res. 2007. PMID: 16674999 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of heparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients with spontaneous intracranial cerebral hemorrhage: a meta-analysis.Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2024 May 22;15:20420986241253469. doi: 10.1177/20420986241253469. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2024. PMID: 38784386 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte as an Independent Predictor of Lower-Extremity Deep Venous Thrombosis in Elderly Patients With Primary Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Front Neurol. 2022 Jul 12;13:899849. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.899849. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35903126 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Machine Learning Techniques to Predict Deep Vein Thrombosis in Rehabilitation Inpatients.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023 Jan-Dec;29:10760296231179438. doi: 10.1177/10760296231179438. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023. PMID: 37365805 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of low molecular weight heparin combined with hyperbaric oxygen on neurologic function and coagulation factors in patients with intracranial venous thrombosis.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Mar 15;14(3):2101-2108. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35422938 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of hydrocolloid dressing combined with low molecular weight heparin and calcium on scar hyperplasia in burn patients with venous thromboembolism.Int Wound J. 2023 Oct;20(8):2981-2988. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14165. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Int Wound J. 2023. PMID: 36960910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang X, Arima H, Heeley E, Delcourt C, Huang Y, Wang J, Stapf C, Robinson T, Woodward M, Chalmers J, Anderson CS INTERACT2 Investigators. Magnitude of blood pressure reduction and clinical outcomes in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: intensive blood pressure reduction in acute cerebral hemorrhage trial study. Hypertension. 2015;65:1026–1032. - PubMed
-
- Xue X, Liu H, Shao D, Zhang W, Ren Y, Sun Z, Lin J, Nie S. Logistic regression analysis on risk factors of cerebral hemorrhage complicated with stress ulcer. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014;26:730–733. - PubMed
-
- Guo R, Blacker DJ, Wang X, Arima H, Lavados PM, Lindley RI, Chalmers J, Anderson CS, Robinson T. Practice patterns for neurosurgical utilization and outcome in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: intensive blood pressure reduction in acute cerebral hemorrhage trials 1 and 2 studies. Neurosurgery. 2017;81:980–985. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
