Clinical nursing pathway improves disease cognition and quality of life of elderly patients with hypertension and cerebral infarction
- PMID: 34650739
- PMCID: PMC8506990
Clinical nursing pathway improves disease cognition and quality of life of elderly patients with hypertension and cerebral infarction
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the application effect of clinical nursing pathway model in elderly patients with hypertension and cerebral infarction.
Methods: A total of 106 elderly patients with hypertension and cerebral infarction were recruited and divided into a control group (n=51) and a test group (n=55). Both groups of patients received conventional care, and the test group was given additional care if clinical nursing pathway. The blood pressure indexes, knowledge of stroke, nursing satisfaction, neurological deficit, and activity of daily living (ADL) of the two groups of patients were observed.
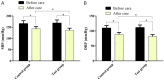
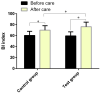
Results: After nursing care, the scores of Stroke Knowledge Questionnaire (SKQ) and Barthel index (BI) increased in both groups, and they were significantly higher in the test group than in the control group. The scores of systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) decreased significantly in both groups after nursing, and they were lower in the test group than the control group. In addition, patients in the test group exhibited higher nursing satisfaction than the control group, as well as higher rates of blood pressure control at discharge, two months, four months and six months after discharge.
Conclusion: The application of clinical nursing pathway can improve the disease cognition and quality of life of elderly patients with hypertension and cerebral infarction, and promote their recovery.
Keywords: Clinical nursing pathway; cerebral infarction; hypertension; quality of life.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of comprehensive care measures based on the HAPA model on self-care, neurotransmitters and clinical outcomes in cerebral infarction patients.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 May;27(10):4462-4470. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202305_32452. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37259727
-
Effects of an evidence-based nursing intervention on neurological function and serum inflammatory cytokines in patients with acute cerebral infarction: A randomized controlled trial.Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2021;39(2):129-137. doi: 10.3233/RNN-201080. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33935121 Clinical Trial.
-
[Effect of " Huoxue Sanfeng acupuncture" auxiliary therapy on morning blood pressure and blood pressure load in elderly patients with stroke complicated with hypertension].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2019 Apr 12;39(4):349-54. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2019.04.002. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2019. PMID: 30957443 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effect Analysis of Clinical Pathway Nursing Combined with Humanized Nursing in Cerebral Infarction.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 11;2022:8270137. doi: 10.1155/2022/8270137. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9797429. doi: 10.1155/2023/9797429. PMID: 35726292 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
[Cognitive function and basic activity of daily living of elderly disabled inpatients].Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2000 Mar;37(3):225-32. doi: 10.3143/geriatrics.37.225. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 10879072 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Construction and application of procedural pathways combined with information management in nursing staff skills training system.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Jun 21;24(1):687. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05593-x. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38907202 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of acupuncture for cerebral infarction from 1993 to 2023.Front Neurol. 2024 May 2;15:1386164. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1386164. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38756219 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a hospital-community-family trinity rehabilitation nursing model combined with motor imagery therapy in patients with cerebral infarction.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Jan 26;11(3):621-628. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i3.621. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 36793630 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of a smartphone-enabled dyadic self-care programme (SDSCP) for stroke survivors and caregivers: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2023 Sep 4;13(9):e073016. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-073016. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37666544 Free PMC article.
-
A novel GJA5 variant associated with increased risk of essential hypertension.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Feb 15;15(2):1259-1270. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36915790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drummond GR, Vinh A, Guzik TJ, Sobey CG. Immune mechanisms of hypertension. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19:517–532. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
