Diallyl sulfide protects against dilated cardiomyopathy via inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice
- PMID: 34651661
- PMCID: PMC8532119
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12492
Diallyl sulfide protects against dilated cardiomyopathy via inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice
Abstract
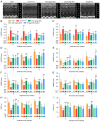
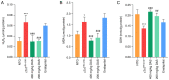
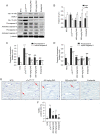
Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily E member 1 (CYP2E1) is a member of the cytochrome P450 enzyme family and catalyzes the metabolism of various substrates. CYP2E1 is upregulated in multiple heart diseases and causes damage mainly via the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). In mice, increased CYP2E1 expression induces cardiac myocyte apoptosis, and knockdown of endogenous CYP2E1 can attenuate the pathological development of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Nevertheless, targeted inhibition of CYP2E1 via the administration of drugs for the treatment of DCM remains elusive. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate whether diallyl sulfide (DAS), a competitive inhibitor of CYP2E1, can be used to inhibit the development of the pathological process of DCM and identify its possible mechanism. Here, cTnTR141W transgenic mice, which developed typical DCM phenotypes, were used. Following treatment with DAS for 6 weeks, echocardiography, histological analysis and molecular marker detection were conducted to investigate the DAS‑induced improvement on myocardial function and morphology. Biochemical analysis, western blotting and TUNEL assays were used to detected ROS production and myocyte apoptosis. It was found that DAS improved the typical DCM phenotypes, including chamber dilation, wall thinning, fibrosis, poor myofibril organization and decreased ventricular blood ejection, as determined using echocardiographic and histopathological analyses. Furthermore, the regulatory mechanisms, including inhibition both of the oxidative stress levels and the mitochondria‑dependent apoptosis pathways, were involved in the effects of DAS. In particular, DAS showed advantages in terms of improved chamber dilation and dysfunction in model mice, and the improvement occurred in the early stage of the treatment compared with enalaprilat, an angiotensin‑converting enzyme inhibitor that has been widely used in the clinical treatment of DCM and HF. The current results demonstrated that DAS could protect against DCM via inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis. These findings also suggest that inhibition of CYP2E1 may be a valuable therapeutic strategy to control the development of heart diseases, especially those associated with CYP2E1 upregulation. Moreover, the development of DAS analogues with lower cytotoxicity and metabolic rate for CYP2E1 may be beneficial.
Keywords: cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily E member 1; diallyl sulfide; dilated cardiomyopathy; inhibitor of CYP2E1; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Knockdown of cytochrome P450 2E1 inhibits oxidative stress and apoptosis in the cTnT(R141W) dilated cardiomyopathy transgenic mice.Hypertension. 2012 Jul;60(1):81-9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.191478. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Hypertension. 2012. PMID: 22665122
-
Expression of CYP2E1 increases oxidative stress and induces apoptosis of cardiomyocytes in transgenic mice.FEBS J. 2011 May;278(9):1484-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08063.x. Epub 2011 Mar 15. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21352494
-
Diallyl Sulfide: Potential Use in Novel Therapeutic Interventions in Alcohol, Drugs, and Disease Mediated Cellular Toxicity by Targeting Cytochrome P450 2E1.Curr Drug Metab. 2015;16(6):486-503. doi: 10.2174/1389200216666150812123554. Curr Drug Metab. 2015. PMID: 26264202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effects of diallyl sulfide, a garlic constituent, on the warm hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model.Pharm Res. 2008 Oct;25(10):2231-42. doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9601-8. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 18626753
-
Mechanisms of inhibition of chemical toxicity and carcinogenesis by diallyl sulfide (DAS) and related compounds from garlic.J Nutr. 2001 Mar;131(3s):1041S-5S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.3.1041S. J Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11238812 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of diagnostic model in heart failure with myocardial fibrosis and conduction block by integrated gene co-expression network analysis.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Feb 14;17(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01814-w. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38355637 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of an evodiamine derivative for PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway activation and AD pathology improvement in mouse models.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Jan 9;15:1025066. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1025066. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36698780 Free PMC article.
-
Kuoxin Decoction Alleviated Left Ventricular Remodeling by Inhibiting Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis Through ASK1/JNK/Cx43 Signaling Pathway in cTnTR141W Transgenic Mice and in vitro.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Aug 4;19:6665-6686. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S517404. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40786250 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin β1/FAK/SRC signal pathway is involved in autism spectrum disorder in Tspan7 knockout rats.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Dec 20;6(3):e202201616. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201616. Print 2023 Mar. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 36625203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murray B, Peng H, Barbier-Torres L, Robinson AE, Li TWH, Fan W, Tomasi ML, Gottlieb RA, Van Eyk J, Lu Z, et al. Methionine adenosyltransferase α1 is targeted to the mitochondrial matrix and interacts with cytochrome P450 2E1 to lower its expression. Hepatology. 2019;70:2018–2034. doi: 10.1002/hep.30762. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

