FABP4 knockdown suppresses inflammation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes by activating PPARγ to regulate the NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 34651666
- PMCID: PMC8532115
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12495
FABP4 knockdown suppresses inflammation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes by activating PPARγ to regulate the NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
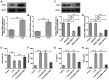
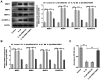
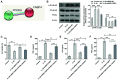
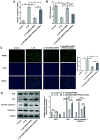
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative disease that can lead to severe joint pain and loss of function, seriously threatening the health and normal life of patients. At present, the pathogenesis of OA remains to be clarified. Recent studies have shown that fatty acid‑binding protein 4 (FABP4) is increased in the plasma and synovial fluid of patients with OA. However, the effect of FABP4 on OA is unclear. The present study established IL‑1β‑induced ATDC5 cells with FABP4 knockdown. Next, cell viability was detected with Cell Counting Kit‑8 assay. The content of inflammatory factors, prostaglandin E2 and glycosaminoglycan (GAG) was detected via ELISA. The levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in cells were detected by using ROS and SOD kits, respectively. TUNEL staining was used to detect the apoptosis level. Western blotting was used to detect the expression levels of proteins. The results revealed that FABP4 was upregulated in IL‑1β‑induced ATDC5 cells. Knockdown of FABP4 increased cell viability, reduced inflammatory damage, oxidative stress and apoptosis in IL‑1β‑induced ATDC5 cells. Following FABP4 knockdown, the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP3, MMP9 and MMP13) of IL‑1β‑induced ATDC5 cells was reduced, and the expression of GAG was promoted. FABP4 knockdown also inhibited the expression of NF‑κB p65 and enhanced peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor (PPAR)γ expression. However, the presence of PPARγ inhibitor blocked the aforementioned effects of FABP4 on IL‑1β‑induced ATDC5 cells. In conclusion, FABP4 knockdown suppressed the inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of IL‑1β‑induced chondrocytes by activating PPARγ to inhibit the NF‑κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: NF-κB signaling pathway; fatty acid-binding protein 4; inflammation; osteoarthritis; peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor γ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fxyd5 activates the NF‑κB pathway and is involved in chondrocytes inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Apr;25(4):134. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12650. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35191523 Free PMC article.
-
FHL2 deteriorates IL-1β induced inflammation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation in chondrocyte-like ATDC5 cells by mTOR and NF-ĸB pathways.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Apr 4;26(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08536-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40186216 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) induces chondrocyte degeneration via activation of the NF-κb signaling pathway.FASEB J. 2024 Jan;38(1):e23347. doi: 10.1096/fj.202301882R. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38095503
-
Betulinic acid inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation by activating PPAR-γ in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Dec;29(2):687-692. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.09.009. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26391061
-
Fatty acid-binding protein 4 in kidney diseases: From mechanisms to clinics.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;931:175224. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175224. Epub 2022 Aug 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35995212 Review.
Cited by
-
MgO@SiO2 nanocapsules: a controlled magnesium ion release system for targeted inhibition of osteoarthritis progression.Nanoscale Adv. 2025 Jan 21;7(7):1814-1824. doi: 10.1039/d4na00900b. eCollection 2025 Mar 25. Nanoscale Adv. 2025. PMID: 39911730 Free PMC article.
-
Tilorone mitigates the propagation of α-synucleinopathy in a midbrain-like organoid model.J Transl Med. 2024 Sep 2;22(1):816. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05551-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39223664 Free PMC article.
-
PDK4 inhibits osteoarthritis progression by activating the PPAR pathway.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Feb 2;19(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04583-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38308345 Free PMC article.
-
GDPD3 Deficiency Alleviates Neuropathic Pain and Reprograms Macrophagic Polarization Through PGE2 and PPARγ Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2024 Aug;49(8):1980-1992. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04148-2. Epub 2024 May 20. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38769197 Free PMC article.
-
FABP4 Mediates Inflammation to Regulate Endometrial Epithelial Cell Function During Early Gestation in Sheep.Vet Med Sci. 2025 Mar;11(2):e70193. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70193. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39999279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boehme KA, Rolauffs B. Onset and Progression of Human Osteoarthritis-Can Growth Factors, Inflammatory Cytokines, or Differential miRNA Expression Concomitantly Induce Proliferation, ECM Degradation, and Inflammation in Articular Cartilage? Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:2282. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082282. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

