Long Noncoding-RNA Component of Mitochondrial RNA Processing Endoribonuclease Promotes Carcinogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via the Competing Endogenous RNA Mechanism
- PMID: 34652079
- PMCID: PMC8561136
- DOI: 10.4048/jbc.2021.24.e42
Long Noncoding-RNA Component of Mitochondrial RNA Processing Endoribonuclease Promotes Carcinogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via the Competing Endogenous RNA Mechanism
Abstract
Purpose: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a subtype of breast cancer. Increasing evidence supports that dysregulation of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) plays a vital role in cancer progression. RNA component of mitochondrial RNA processing endoribonuclease (RMRP), a lncRNA, is characterized as a tumor-propeller in some cancers, but its mechanism in TNBC remains poorly understood. This study aimed to determine whether and how RMRP functions in TNBC.
Methods: Cell proliferation was determined by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and colony formation assays and cell apoptosis by flow cytometry analysis and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Cell migration and invasion were determined by transwell assays. RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP), luciferase reporter, and RNA pulldown assays were implemented to assess the interaction of RMRP with other molecules in TNBC cells.
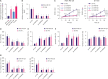
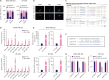
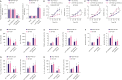
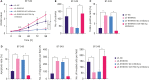
Results: RMRP expression was elevated in TNBC cells. RMRP knockdown repressed cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, but induced apoptosis in TNBC. In addition, RMRP was found to target microRNA-766-5p (miR-766-5p) in TNBC cells. Silencing miR-766-5p enhanced cell viability and decreased apoptosis, whereas miR-766-5p overexpression had opposite effects. Furthermore, miR-766-5p was found to bind to yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1). Moreover, miR-766-5p inhibition reversed the repressive effect of RMRP knockdown on the malignant progression of TNBC.
Conclusion: The present study manifested that RMRP promotes the growth, migration, and invasion of TNBC cells via the miR-766-5p/YAP1 axis. These findings provide novel perspectives for TNBC treatment.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; MicroRNAs; RNA, untranslated; Triple negative breast neoplasms.
© 2021 Korean Breast Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
lncRNA MIR503HG inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in TNBC cells via the miR-224-5p/HOXA9 axis.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021 Mar 17;21:62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.03.009. eCollection 2021 Jun 25. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021. PMID: 33869743 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HCP5 promotes triple negative breast cancer progression as a ceRNA to regulate BIRC3 by sponging miR-219a-5p.Cancer Med. 2019 Aug;8(9):4389-4403. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2335. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31215169 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA RMRP knockdown promotes proliferation and migration of Schwann cells by mediating the miR-766-5p/CAND1 axis.Neurosci Lett. 2022 Jan 23;770:136440. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136440. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Neurosci Lett. 2022. PMID: 34974108
-
TCF3-activated FAM201A enhances cell proliferation and invasion via miR-186-5p/TNKS1BP1 axis in triple-negative breast cancer.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Nov;104:104301. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104301. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33011533
-
Long non-coding RNA SNHG8 enhances triple-negative breast cancer cell proliferation and migration by regulating the miR-335-5p/PYGO2 axis.Biol Direct. 2021 Aug 6;16(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13062-021-00295-6. Biol Direct. 2021. PMID: 34362407 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nanomaterial-assisted CRISPR gene-engineering - A hallmark for triple-negative breast cancer therapeutics advancement.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Oct 4;16:100450. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100450. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36267139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and Significance of LINC02418 in Breast Cancer.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024 Apr 24;16:233-243. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S454054. eCollection 2024. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024. PMID: 38694704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peart O. Breast intervention and breast cancer treatment options. Radiol Technol. 2015;86:535M–558M. - PubMed
-
- Hwang SY, Park S, Kwon Y. Recent therapeutic trends and promising targets in triple negative breast cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;199:30–57. - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Wu WB, Wang ZW, Wang XH. lncRNA NEAT1 is closely related with progression of breast cancer via promoting proliferation and EMT. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:1020–1026. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

