Early cross-coronavirus reactive signatures of humoral immunity against COVID-19
- PMID: 34652962
- PMCID: PMC8943686
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abj2901
Early cross-coronavirus reactive signatures of humoral immunity against COVID-19
Abstract
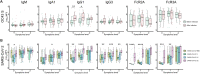
The introduction of vaccines has inspired hope in the battle against SARS-CoV-2. However, the emergence of viral variants, in the absence of potent antivirals, has left the world struggling with the uncertain nature of this disease. Antibodies currently represent the strongest correlate of immunity against SARS-CoV-2, thus we profiled the earliest humoral signatures in a large cohort of acutely ill (survivors and nonsurvivors) and mild or asymptomatic individuals with COVID-19. Although a SARS-CoV-2–specific immune response evolved rapidly in survivors of COVID-19, nonsurvivors exhibited blunted and delayed humoral immune evolution, particularly with respect to S2-specific antibodies. Given the conservation of S2 across β-coronaviruses, we found that the early development of SARS-CoV-2–specific immunity occurred in tandem with preexisting common β-coronavirus OC43 humoral immunity in survivors, which was also selectively expanded in individuals that develop a paucisymptomatic infection. These data point to the importance of cross-coronavirus immunity as a correlate of protection against COVID-19.
Figures

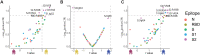

Update of
-
Early cross-coronavirus reactive signatures of protective humoral immunity against COVID-19.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 May 12:2021.05.11.443609. doi: 10.1101/2021.05.11.443609. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: Sci Immunol. 2021 Oct 15;6(64):eabj2901. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abj2901. PMID: 34013263 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Jackson L. A., Anderson E. J., Rouphael N. G., Roberts P. C., Makhene M., Coler R. N., McCullough M., Chappell J. D., Denison M. R., Stevens L. J., Pruijssers A. J., McDermott A., Flach B., Doria-Rose N. A., Corbett K. S., Morabito K. M., O'Dell S., Schmidt S. D., Swanson P. A. II, Padilla M., Mascola J. R., Neuzil K. M., Bennett H., Sun W., Peters E., Makowski M., Albert J., Cross K., Buchanan W., Pikaart-Tautges R., Ledgerwood J. E., Graham B. S., Beigel J. H.; mRNA-1273 Study Group , An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 - Preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1920–1931 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Polack F. P., Thomas S. J., Kitchin N., Absalon J., Gurtman A., Lockhart S., Perez J. L., Pérez Marc G., Moreira E. D., Zerbini C., Bailey R., Swanson K. A., Roychoudhury S., Koury K., Li P., Kalina W. V., Cooper D., Frenck R. W. Jr, Hammitt L. L., Türeci Ö., Nell H., Schaefer A., Ünal S., Tresnan D. B., Mather S., Dormitzer P. R., Şahin U., Jansen K. U., Gruber W. C.; C4591001 Clinical Trial Group , Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 2603–2615 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klingler J., Lambert G. S., Itri V., Liu S., Bandres J. C., Enyindah-Asonye G., Liu X., Oguntuyo K. Y., Amanat F., Lee B., Zolla-Pazner S., Upadhyay C., Hioe C. E., SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines induce a greater array of spike-specific antibody isotypes with more potent complement binding capacity than natural infection. medRxiv 2021.05.11.21256972 (2021).
-
- Chen R. E., Zhang X., Case J. B., Winkler E. S., Liu Y., VanBlargan L. A., Liu J., Errico J. M., Xie X., Suryadevara N., Gilchuk P., Zost S. J., Tahan S., Droit L., Turner J. S., Kim W., Schmitz A. J., Thapa M., Wang D., Boon A. C. M., Presti R. M., O’Halloran J. A., Kim A. H. J., Deepak P., Pinto D., Fremont D. H., Crowe J. E. Jr., Corti D., Virgin H. W., Ellebedy A. H., Shi P. Y., Diamond M. S., Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and serum-derived polyclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 27, 717–726 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

