Assessment of the Clinical Utility of Circulating Tumor Cells at Different Time Points in Predicting Prognosis of Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34654345
- PMCID: PMC8521771
- DOI: 10.1177/10732748211050581
Assessment of the Clinical Utility of Circulating Tumor Cells at Different Time Points in Predicting Prognosis of Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Numerous studies have elucidated that circulating tumor cells (CTCs) have significant prognostic value in various solid tumors. However, the prognostic value of CTCs in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) remains controversial. The current study was performed to investigate the prognostic significance of different time points of CTCs in SCLC.
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases were retrieved for eligible studies. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to investigate the association between CTCs level and overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) in SCLC. Furthermore, subgroup analyses, sensitivity analysis, Begg's and Egger's tests were also conducted.
Results: Sixteen cohort studies with 1103 participants were eligible for this meta-analysis. Our results revealed that higher pretreatment CTCs level was significantly correlated with worse OS in SCLC no matter CellSearch (HR, 2.95; 95%CI, 1.56-5.58; P = .001) or other methods (HR, 2.37; 95%CI, 1.13-4.99; P = .023) was used to detect CTCs. Higher pretreatment CTCs status detected by CellSearch was associated with shorter PFS (HR, 3.75; 95%CI, 2.52-5.57; P < .001), while there was no significant association when other methods were adopted to CTC detection (HR, 2.04; 95%CI, .73-5.68; P = .172). Likewise, we observed that higher post-therapy CTCs level detected by both CellSearch (HR, 2.99; 95%CI, 1.51-5.93; P = .002) and other methods (HR, 4.79; 95%CI, 2.03-11.32; P < .001) was significantly correlated with decreased OS in SCLC. However, higher post-therapy CTCs count detected by CellSearch was not correlated with worse PFS (HR, 1.80; 95%CI, .83-3.90; P = .135). Sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the pooled data were still stable after eliminating studies one by one. However, significant publication bias was observed between pretreatment CTCs level detected by CellSearch and OS of SCLC.
Conclusion: Dynamic monitoring of CTCs level could be a non-invasive and effective tool to predict the disease progression and prognosis in patients with SCLC.
Keywords: circulating tumor cells; meta-analysis; prognosis; small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
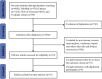

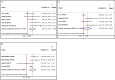
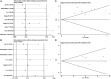
Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression on circulating tumor cells in various cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2021 Oct;10(20):7021-7039. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4236. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34423578 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of circulating tumour cells in limited-stage small-cell lung cancer: analysis of the concurrent once-daily versus twice-daily radiotherapy (CONVERT) randomised controlled trial.Ann Oncol. 2019 Jul 1;30(7):1114-1120. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz122. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31020334 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The detection of circulating tumor cells indicates poor therapeutic efficacy and prognosis in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Evid Based Med. 2024 Jun;17(2):329-340. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12606. Epub 2024 Apr 10. J Evid Based Med. 2024. PMID: 38600712
-
Prognostic impact of circulating tumor cells in patients with small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2012 Mar;7(3):512-9. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31823f125d. J Thorac Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22258473
-
Predictive and prognostic value of folate receptor-positive circulating tumor cells in small cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line chemotherapy.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):49044-49052. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17039. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28467771 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Circulating Tumour Cells - complementary liquid biopsies or standalone concepts?Theranostics. 2022 Aug 1;12(13):5836-5855. doi: 10.7150/thno.73400. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35966579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and safety of anlotinib combined with platinum-etoposide chemotherapy as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A Chinese multicenter real-world study.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 20;12:894835. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.894835. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36203439 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble biomarkers to predict clinical outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer treated by immune checkpoints inhibitors.Front Immunol. 2023 May 22;14:1171649. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1171649. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37283751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating tumor cells: advancing personalized therapy in small cell lung cancer patients.Mol Oncol. 2025 Jul;19(7):1998-2013. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13696. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Mol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 38956984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redefining cancer care: harnessing circulating tumor cells' potential for improved diagnosis and prognosis.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Jul 17;25(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03883-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40676582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shepherd FA, Crowley J, Van Houtte P, et al.. The international association for the study of lung cancer lung cancer staging project: proposals regarding the clinical staging of small cell lung cancer in the forthcoming (Seventh) Edition of the tumor, node, metastasis classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2:1067-1077. - PubMed
-
- Hong S, Zhou T, Fang W, et al.. The prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts overall survival of small-cell lung cancer patients. Tumor Biol. 2015;36:3389-3397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

