Transcriptome and de novo analysis of Rosa xanthina f. spontanea in response to cold stress
- PMID: 34654360
- PMCID: PMC8518255
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-021-03246-5
Transcriptome and de novo analysis of Rosa xanthina f. spontanea in response to cold stress
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Transcriptome and de novo analysis of Rosa xanthina f. spontanea in response to cold stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Dec 30;21(1):606. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03338-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34965866 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Rose is one of most popular ornamental plants worldwide and is of high economic value and great cultural importance. However, cold damage restricts its planting application in cold areas. To elucidate the metabolic response of rose under low temperature stress, we conducted transcriptome and de novo analysis of Rosa xanthina f. spontanea.
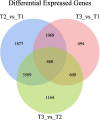
Results: A total of 124,106 unigenes from 9 libraries were generated by de novo assembly, with N50 length was 1470 bp, under 4 °C and - 20 °C stress (23 °C was used as a control). Functional annotation and prediction analyses identified 55,084 unigenes, and 67.72% of these unigenes had significant similarity (BLAST, E ≤ 10- 5) to those in the public databases. A total of 3031 genes were upregulated and 3891 were downregulated at 4 °C compared with 23 °C, and 867 genes were upregulated and 1763 were downregulated at - 20 °C compared with 23 °C. A total of 468 common DEGs were detected under cold stress, and the matched DEGs were involved in three functional categories: biological process (58.45%), cellular component (11.27%) and molecular function (30.28%). Based on KEGG functional annotations, four pathways were significantly enriched: metabolic pathway, response to plant pathogen interaction (32 genes); starch and sucrose metabolism (21 genes); circadian rhythm plant (8 genes); and photosynthesis antenna proteins (7 genes).
Conclusions: Our study is the first to report the response to cold stress at the transcriptome level in R. xanthina f. spontanea. The results can help to elucidate the molecular mechanism of cold resistance in rose and provide new insights and candidate genes for genetically enhancing cold stress tolerance.
Keywords: DEGs; Low-temperature stress; Metabolic pathway; Rose.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
De novo transcriptome sequencing and gene expression profiling of Magnolia wufengensis in response to cold stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Jul 18;19(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1933-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31319815 Free PMC article.
-
De novo sequencing and transcriptome analysis of the desert shrub, Ammopiptanthus mongolicus, during cold acclimation using Illumina/Solexa.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jul 18;14:488. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-488. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23865740 Free PMC article.
-
Global Transcriptome Profiles of 'Meyer' Zoysiagrass in Response to Cold Stress.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 26;10(6):e0131153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131153. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26115186 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly and analysis of the transcriptome of Ocimum americanum var. pilosum under cold stress.BMC Genomics. 2016 Mar 9;17:209. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2507-7. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26955811 Free PMC article.
-
De novo transcriptome assembly and comparative transcriptomic analysis provide molecular insights into low temperature stress response of Canarium album.Sci Rep. 2021 May 18;11(1):10561. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90011-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34006894 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the Rose SWEET Gene Family and Their Different Expression Profiles in Cold Response between Two Rose Species.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;12(7):1474. doi: 10.3390/plants12071474. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050100 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis revealed molecular basis of cold response in Prunus mume.Mol Breed. 2023 Apr 22;43(5):34. doi: 10.1007/s11032-023-01376-2. eCollection 2023 May. Mol Breed. 2023. PMID: 37312744 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals a coordinated mechanism activated in response to cold acclimation in common vetch (Vicia sativa L.).BMC Genomics. 2022 Dec 8;23(1):814. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-09039-w. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36482290 Free PMC article.
-
Correction to: Transcriptome and de novo analysis of Rosa xanthina f. spontanea in response to cold stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Dec 30;21(1):606. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03338-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34965866 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Seimatosporium chinense, a Novel Pestalotioid Fungus Associated with Yellow Rose Branch Canker Disease.Pathogens. 2024 Dec 10;13(12):1090. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13121090. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39770350 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

