Selection strategy of dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute or chronic colitis mouse models based on gut microbial profile
- PMID: 34654370
- PMCID: PMC8520286
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-021-02342-8
Selection strategy of dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute or chronic colitis mouse models based on gut microbial profile
Abstract
Background: Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) replicates ulcerative colitis (UC)-like colitis in murine models. However, the microbial characteristics of DSS-triggered colitis require further clarification. To analyze the changes in gut microbiota associated with DSS-induced acute and chronic colitis.
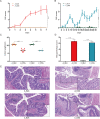
Methods: Acute colitis was induced in mice by administering 3% DSS for 1 week in the drinking water, and chronic colitis was induced by supplementing drinking water with 2.5% DSS every other week for 5 weeks. Control groups received the same drinking water without DSS supplementation. The histopathological score and length of the colons, and disease activity index (DAI) were evaluated to confirm the presence of experimental colitis. Intestinal microbiota was profiled by 16S rDNA sequencing of cecal content.
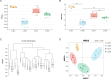
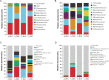
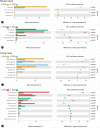
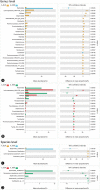
Results: Mice with both acute and chronic DSS-triggered colitis had significantly higher DAI and colon histopathological scores in contrast to the control groups (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001), and the colon was remarkably shortened (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001). The gut microbiota α-diversity was partly downregulated in both acute and chronic colitis groups in contrast to their respective control groups (Pielou index P = 0.0022, P = 0.0649; Shannon index P = 0.0022, P = 0.0931). The reduction in the Pielou and Shannon indices were more obvious in mice with acute colitis (P = 0.0022, P = 0.0043). The relative abundance of Bacteroides and Turicibacter was increased (all P < 0.05), while that of Lachnospiraceae, Ruminococcaceae, Ruminiclostridium, Rikenella, Alistipes, Alloprevotella, and Butyricicoccus was significantly decreased after acute DSS induction (all P < 0.05). The relative abundance of Bacteroides, Akkermansia, Helicobacter, Parabacteroides, Erysipelatoclostridium, Turicibacter and Romboutsia was also markedly increased (all P < 0.05), and that of Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, Alistipes, Enterorhabdus, Prevotellaceae_UCG-001, Butyricicoccus, Ruminiclostridium_6, Muribaculum, Ruminococcaceae_NK4A214_group, Family_XIII_UCG-001 and Flavonifractor was significantly decreased after chronic DSS induction (all P < 0.05).
Conclusion: DSS-induced acute and chronic colitis demonstrated similar symptoms and histopathological changes. The changes in the gut microbiota of the acute colitis model were closer to that observed in UC. The acute colitis model had greater abundance of SCFAs-producing bacteria and lower α-diversity compared to the chronic colitis model.
Keywords: Acute colitis; Chronic colitis; Dextran sulfate sodium; Gut microbiota.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

