Multivariate analysis of factors associated with spinal cord area in single-door cervical laminoplasty with miniplate fixation
- PMID: 34654410
- PMCID: PMC8520309
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-021-04773-w
Multivariate analysis of factors associated with spinal cord area in single-door cervical laminoplasty with miniplate fixation
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the factors associated with the increased spinal cord area in single-door cervical laminoplasty (SDCL) with miniplate fixation.
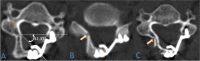
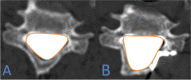
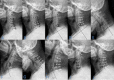
Methods: A retrospective study enrolled 83 patients underwent SDCL with miniplate fixation and the patient characteristics such as age, gender, tobacco use, alcohol use, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, diagnosis, operative level, etc., were obtained. The opening angle, door shaft position and spinal canal area of the patients were measured after surgery. The sagittal canal diameter (SCD), the C2-7 Cobb angle, the cervical curvature index (CCI), the range of motion (ROM) and the spinal canal area were measured before and after operation. The increased cervical spinal cord area was also measured before and after surgery, and the correlation between the above indicators and the increased cervical spinal cord area was studied through Pearson's correlation analysis and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Results: There were 34 patients in small spinal cord area increment group (SAI group), 29 patients in middle spinal cord area increment group (MAI group) and 20 patients in large spinal cord area increment group (LAI group). The preoperative diagnosis(P = 0.001), door shaft position (P = 0.008), preoperative spinal canal area (P = 0.004) and postoperative spinal canal area (P = 0.015) were significant different among the 3 groups. The multivariate analysis showed that the preoperative diagnosis (OR = 2.076, P = 0.035), door shaft position (OR = 3.425, P = 0.020) and preoperative spinal canal area (OR = 10.217, P = 0.009) were related to increased spinal cord area.
Conclusions: The preoperative diagnosis, door shaft position and preoperative spinal canal area might be associated with increased spinal cord area after cervical laminoplasty with miniplate fixation. Preoperative symptoms are mostly caused by compression of the spinal cord, so spinal cord area enlargement can bring a better recovery in patients alongside long-term. Spine surgeons should pay more attention to the accuracy of the preoperative diagnosis, the preoperative measurement of spinal canal area and the door shaft position during the operation.
Keywords: Door shaft position; Single-door cervical laminoplasty; Spinal canal area; Spinal cord area.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is there any correlation between the recovery rate of JOA and the increasing of cervical spinal cord area after single-door cervical laminoplasty?Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022 Feb;213:107103. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2021.107103. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 34959107
-
Prediction of spinal canal expansion following cervical laminoplasty: a computer-simulated comparison between single and double-door techniques.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006 Nov 15;31(24):2863-70. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000245851.55012.f1. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006. PMID: 17108843
-
Multivariate Analysis of Factors Associated With Axial Symptoms in Unilateral Expansive Open-Door Cervical Laminoplasty With Miniplate Fixation.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(2):e2292. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002292. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26765404 Free PMC article.
-
[The dorsal approach in degeneratively changed cervical spine].Orthopade. 1996 Nov;25(6):533-41. doi: 10.1007/s001320050057. Orthopade. 1996. PMID: 8999408 Review. German.
-
Cervical alignment and range of motion after laminoplasty: radiographical data from more than 500 cases with cervical spondylotic myelopathy and a review of the literature.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Sep 15;37(20):E1243-50. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182659d3e. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012. PMID: 22739671 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive value of dynamic diffusion tensor imaging for surgical outcomes in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Oct 1;24(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01428-9. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39354411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsumoto M, Watanabe K, Hosogane N, Tsuji T, Ishii K, Nakamura M, et al. Impact of lamina closure on long-term outcomes of open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy: minimum 5-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37(15):1288–1291. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182498434. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

